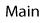Vertebrate Wnt genes
- In the following table, the red diamond ♦ indicates that the particular Wnt gene has been identified.
- There are additional tables for each species and a separate table for syntenic linkage groups for
mouse and human genes. See the
footnotes for more info.
- See alignments Wnts
Comparative table of all vertebrate Wnt genes
gene |
Mouse |
Human |
Xenopus |
Chicken |
Zebrafish |
| Wnt1 |
|
♦ | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
| Wnt2 | ♦ | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
|
| Wnt2B |
|
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
|
| Wnt3 | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
|
| Wnt3A | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
|
| Wnt4 | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
| Wnt4B | ♦ |
||||
| Wnt5A | ♦ |
|
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
| Wnt5B | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
||
| Wnt6 | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
||
| Wnt7A | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
| Wnt7B | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
|
| Wnt7C | ♦ |
||||
| gene | Mouse | Human | Xenopus | Chicken | Zebrafish |
| Wnt8A | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
| Wnt8B | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
| Wnt9A | ♦ | ♦ |
♦ | ♦ |
|
| Wnt9B | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ | |
|
| Wnt10A | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
|
| Wnt10B | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ | ♦ |
|
| Wnt11 | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
♦ |
| Wnt12, Wnt13, Wnt14, Wnt15 have all been renamed, see below | |||||
| Wnt-16 | ♦ |
♦ |
♦ | ||
notes
1. A gene called Wnt-12 identified by Adamson et al is the same as reported by Lee et al, Hardiman et al, and Wang and Shackleford; and called Wnt-10B. As this mouse Wnt gene is indeed very similar to Wnt-10 genes cloned from Xenopus and Zebrafish (Wolda, S. L. and Moon, R. T. (1992) and it should be called Wnt-10B.
2. The gene called human Wnt-13 (Katoh et al, 1996) is very similar to the human Wnt-2 and is better named Wnt-2B. The first Wnt-2 cloned from Xenopus is called XWnt-2 Wolda, S. L. and Moon, R. T. (1992) but it is the ortholog of Wnt-2B/Wnt13. A Xenopus Wnt-2 cloned by Landesman Y and Sokol SY (1997) is called XWnt-2B, but is actually the ortholog of the human and mouse Wnt-2.
3. The chicken Wnt-8C is probably the true ortholog of Xenopus Wnt-8A, as these genes are very similar. In addition, there are no other chicken Wnt-8 genes yet, nor have separate orthologs of CWnt-8C been cloned from the mouse and the human.
4. Wnt9 was initially only isolated from Hagfish (Eptatretus stouti) and Thresher Shark (Alopius vulpinus) Sidow 1992. It was realized by Qian et al (2003) that the genes first called Wnt14 and Wnt15 are orthologs of Wnt9. Wnt14 and Wnt15 have therefore been renamed into Wnt9A and Wnt9B.