MTSOS: BLAS tips
BLAS stands for Basic Linear Algebra Subroutines and is a library of linear algebra subroutines that have been optimized for a particular system. Thus rather than manually writing out these operators one can call the BLAS subroutine as they have been optimized with respect to hardware to perform much faster. Many systems already include BLAS (for example LAPACK includes BLAS, and most Mac releases) but if not, one can download an optimized implementation which can be found from the BLAS page or it can be compiled using ATLAS. Aside from being necessary for MTSOS, many users may want to use these functions in their custom barrier and dynamics functions. Below we explain the BLAS interface for C that is provided with MATLAB, which is also the interface used by most Mac implementations, for several useful functions.
NOTE: This interface is different from the ATLAS ANSI/ISO C BLAS API Reference which will result from ATLAS, and different from the C interface in the BLAS Standard. Should a BLAS library with a different interface be used, modifications may be necessary to the MTSOS code (there are three calls to dgemv in MTSOS.c).
dgemv
Calculates 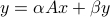 . Note that ptrdiff_t is the result of pointer subtraction, and can be considered an int.
. Note that ptrdiff_t is the result of pointer subtraction, and can be considered an int.
- void dgemv( char* trans, ptrdiff_t* m, ptrdiff_t*n, double* alpha,
double* A, ptrdiff_t* lda, double* x, ptrdiff_t* incx, double* beta,
double* y, ptrdiff_t* incy)
| char* trans | N: matrix A is provided in column first order T: matrix A is provided in row order (alternatively, this will take the transpose of A) |
| ptrdiff_t* m | the number of rows in 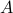 |
| ptrdiff_t* n | the number of columns in 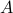 |
| double* alpha | 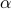 |
| double* A | an array that is a column first (if you set trans = N) representation of 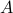 |
| ptrdiff_t* lda | typically m (the number of rows in 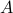 ); ); 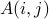 is found at A[i + lda*j] (assuming indices start at 0) is found at A[i + lda*j] (assuming indices start at 0) |
| double* x | an array with the value of 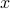 |
| ptrdiff_t* incx | typically 1; the value of 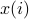 is found at x[i*incx] is found at x[i*incx] |
| double* beta | 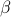 ; if only ; if only 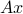 is desired, set to zero is desired, set to zero |
| double* y | an array with the value of 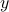 in which the solution will be stored; must be at least size m in which the solution will be stored; must be at least size m |
| ptrdiff_t* incy | typically 1; the value of 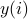 is found at y[i*incy] is found at y[i*incy]
|
dsyr
Calculates 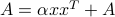 where
where 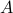 is symmetric.
Note that ptrdiff_t is the result of pointer subtraction can can be considered an int.
is symmetric.
Note that ptrdiff_t is the result of pointer subtraction can can be considered an int.
| char* uplo | L: the solution and values of 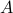 are stored in the lower triangular portion of the matrix are stored in the lower triangular portion of the matrixU: the solution and values of 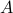 are stored in the upper triangular portion of the matrix are stored in the upper triangular portion of the matrix |
| ptrdiff_t* n | the length of the vector 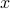 |
| double* alpha | 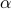 |
| double* x | an array with the value of 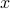 |
| ptrdiff_t* incx | an integer such that 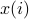 can be found at x[i*incx] can be found at x[i*incx] |
| double* A | a length 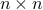 array where the values of array where the values of 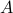 are either stored in the indices corresponding to a lower triangular matrix (uplo = L) or an upper triangular matrix (uplo = U); this is also the array that will store the soluiton are either stored in the indices corresponding to a lower triangular matrix (uplo = L) or an upper triangular matrix (uplo = U); this is also the array that will store the soluiton |
| ptrdiff_t* lda | an integer such that 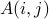 is found at A[i+lda*j] is found at A[i+lda*j]
|
dgemm
Calculates 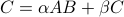 .
Note that ptrdiff_t is the result of pointer subtraction can can be considered an int.
.
Note that ptrdiff_t is the result of pointer subtraction can can be considered an int.
| char* transa | N: matrix A is provided in column first order T: matrix A is provided in row order (alternatively, this will take the transpose of A) |
| char* transb | N: matrix B is provided in column first order T: matrix B is provided in row order (alternatively, this will take the transpose of B) |
| ptrdiff_t* m | the number of rows in 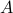 (if transa = N) (if transa = N) |
| ptrdiff_t* n | the number of columns in 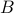 (if transb = N) (if transb = N) |
| ptrdiff_t* k | the number of columns in 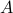 and by association the number of rows in and by association the number of rows in 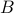 (assuming transa = transb = N (assuming transa = transb = N |
| double* alpha | 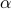 |
| double* a | a size m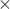 k array representing k array representing 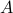 |
| ptrdiff_t* lda | typically, m; an integer such that 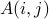 can be found at A[i+lda*j] can be found at A[i+lda*j] |
| double* b | a size k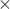 n array representing n array representing 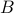 |
| ptrdiff_t* ldb | typically, k; an integer such that 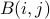 can be found at B[i+ldb*j] can be found at B[i+ldb*j] |
| double* beta | 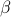 |
| double* c | a size m n array representing n array representing 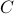 (column first); this matrix will be overwritten to contain the solution (column first); this matrix will be overwritten to contain the solution |
| ptrdiff_t* ldc | typically, m; an integer such that the 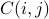 is found at C[i+ldc*j] is found at C[i+ldc*j]
|