MTSOS: writing barrier functions
In order to compile MTSOS, the user must provide a function for calculating the barrier at a given a point 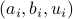 . Although it is possible to write the barrier funciton in MATLAB, doing so will incur a significant performance penalty, so users are encouraged to write their barrier function directly in C.
. Although it is possible to write the barrier funciton in MATLAB, doing so will incur a significant performance penalty, so users are encouraged to write their barrier function directly in C.
A very brief introduction to barrier methods
A very brief introduction to barrier methods will be provided here and we will obscure many of the details to focus on implementation.
For more information on barrier functions for interior point methods see Convex Optimization  and
and  .
.
As outlined in Minimum-Time Speed Optimization Over a Fixed Path the constraints will have the form
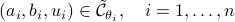 .
.
For the purposes of explanation we will consider constraints of the more specific form
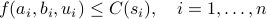 ,
,
where 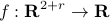 is convex.
is convex.
In a barrier method, we reformulate our constraints as a cost in the objective by adding 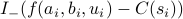 to the objective, where
to the objective, where
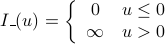
is the indicator function. If the constraint is satisfied, it will not contribute to the objective at all, while if it is unsatisfied, the objective will be infinite. Therefore, to minimize the objective, the constraints must be satisfied. Unfortunately, the indictaor is not differentiable so we approximate it by
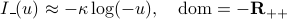 ,
,
where 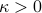 is a parameter that sets the accuracy of the approximation.
As
is a parameter that sets the accuracy of the approximation.
As  decreases, this approximation approaches the indicator function.
Although we strongly encourage the use of the log barrier function, MTSOS is written to allow the use of an alternative barrier function if desired.
If you have multiple constraints, say
decreases, this approximation approaches the indicator function.
Although we strongly encourage the use of the log barrier function, MTSOS is written to allow the use of an alternative barrier function if desired.
If you have multiple constraints, say 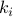 of them at evaluation point
of them at evaluation point 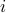 , then we evaluate them as
, then we evaluate them as
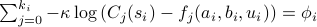 .
.
In the barrier function you must calculate 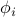 ,
, 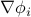 , and
, and 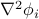 as described below.
as described below.
MATLAB
If the user must write the barrier function in MATLAB, change the compiler to point to barreir_matlab.c instead of barrier_front.c. This will cause the algorithm to look to barrier_mat.m for the dynamics. The name of this file can be changed in barrier_matlab.c.
[H G F] = barrier(S, S_prime, S_dprime, a, b, u,indicator,kappa,variables)
Inputs
| S | a 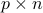 matrix of points where the barrier function must be evaluated matrix of points where the barrier function must be evaluated |
| S_prime | a 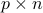 matrix of derivatives of matrix of derivatives of  with respect to with respect to 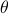 , evaulated at the same points as S , evaulated at the same points as S |
| S_dprime | a 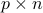 matrix of second derivatives of matrix of second derivatives of  with respect to with respect to 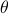 evaluated at the same points as S evaluated at the same points as S |
| b | a vector of the values 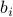 for for 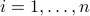 ; the term ; the term 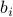 is needed to calculate is needed to calculate 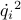 if it is necessary; in particular if it is necessary; in particular 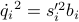 |
| a | a vector of the values of 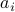 for for 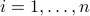 ; the term ; the term 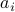 is needed to calculate is needed to calculate 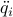 if it is necessary; in particular if it is necessary; in particular 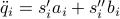 |
| u | an 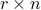 matrix containing the matrix containing the 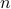 , , 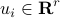 corresponding to the control inputs corresponding to the control inputs |
| indicator | an integer that can take on values between 0 and 3 signifying which terms need to be calculated 0 : Hessian and gradient are required 1 : only the Hessian is required 2 : only the gradient is required 3 : only 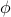 is required is required |
| kappa |  , used in the calculation of , used in the calculation of 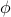 |
| variables | a vector provided by the user at the call to MTSOS in the optional parameter variables |
Outputs
| H | a length 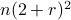 vector consisting of the Hessian of each vector consisting of the Hessian of each 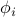 for for 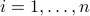 provided in column first order and concatenated; if any of the points lie outside the domain of provided in column first order and concatenated; if any of the points lie outside the domain of 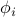 for any for any 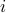 , then H should be set to inf , then H should be set to infNOTE: variable order is 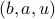 |
| G | a length 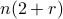 vector consisting of the gradient of each vector consisting of the gradient of each 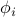 for for 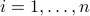 concatenated;if any of the points lie outside the domain of concatenated;if any of the points lie outside the domain of 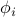 for any for any 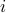 , then G should be set to inf , then G should be set to infNOTE: variable order is 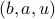 |
| F | a length 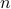 vector consisting of the evaluation of vector consisting of the evaluation of 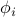 for for 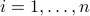 ; if any of the points lie outside the domain of ; if any of the points lie outside the domain of 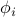 for any for any 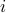 , then G should be set to inf , then G should be set to inf
|
C
- int so_barrier(const double* S, const double* S_prime, const double* S_dprime,
const double* b, const double* a, const double* u,
int S_length, int U_size, int State_size,
int indicator, double kappa, const double* variables, int variables_length,
double* H_barrier, double* G_barrier, double* F_barrier)
Inputs
Note: these are all constant.
| double* S | a length 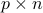 array of points where the barrier function must be evaluated array of points where the barrier function must be evaluated |
| double* S_prime | a length 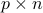 array of the derivative of array of the derivative of  with respect to with respect to 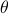 , evaluated at the same points as S , evaluated at the same points as S |
| double* S_dprime | a length 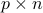 array of the second derivative of array of the second derivative of  with respect to with respect to 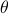 , evaluated at the same points as S , evaluated at the same points as S |
| double* b | a length 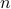 array of the values of array of the values of 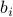 for for 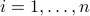 ; the term ; the term 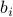 is needed to calculate is needed to calculate 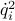 if it is necessary; in particular if it is necessary; in particular 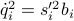 |
| double* a | a length 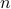 array of the values of array of the values of 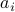 for for 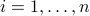 ;the term ;the term 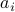 is needed to calculate is needed to calculate 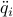 if it is necessary: if it is necessary: 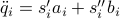 |
| double* u | a length 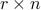 array containing the array containing the 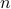 , , 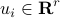 corresponding to the control inputs at each epoch concatenated corresponding to the control inputs at each epoch concatenated |
| int S_length | 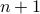 , the number of discretization points , the number of discretization points |
| int U_size |  , the number of control inputs , the number of control inputs |
| int State_size | 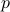 , the size of the configuration space , the size of the configuration space |
| int indicator | an integer that can take on values between 0 and 3 signifying which terms need to be calculated 0 : Hessian and gradient are required 1 : only the Hessian is required 2 : only the gradient is required 3 : only 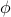 is required is required |
| double kappa |  , used in the calculation of , used in the calculation of 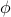 |
| double* variables | an array provided by the user at the call to MTSOS in the optional parameter variables |
| int variables_length | the length of the array variables |
Outputs
Allocated, but unitialized, arrays are provided for the user to populate. In particular, if an array needs to be zero, the values must be set to zero, do not assume any values in the arrays.
| RETURN int | 1 : all values are within the domain, no errors 0 : points lie outside the domain of 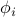 -1 : an error occurred and the algorithm will abort |
| double* H_barrier | a length 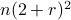 array consisting of the Hessian for each array consisting of the Hessian for each 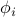 for for 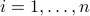 provided in column first order and concatenated; if any of the points lie outside the domain of provided in column first order and concatenated; if any of the points lie outside the domain of 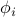 for any for any 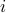 , then the value of H_barrier is irrelevant and the function should return 0 , then the value of H_barrier is irrelevant and the function should return 0 |
| double* G_barrier | a length 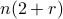 array consisting of the gradient of each array consisting of the gradient of each 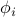 for for 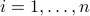 concatenated; if any of the points lie outside the domain of concatenated; if any of the points lie outside the domain of 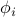 for any for any 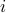 , then the value of G_barrier is irrelevant and the function should return 0 , then the value of G_barrier is irrelevant and the function should return 0 |
| double* F_barrier | a length 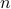 array consisting of the evaluation of array consisting of the evaluation of 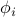 for for 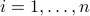 ; if any of the points lie outside the domain of ; if any of the points lie outside the domain of 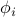 for any for any 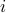 , then the value of F_barrier is irrelevant and the function should return 0 , then the value of F_barrier is irrelevant and the function should return 0
|
Tips for writing barrier functions
Log barrier gradients and Hessians
Some useful quantities when using the log barrier function,
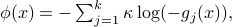 are:
are:
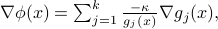
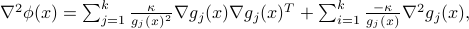
where 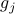 is
is 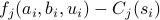 .
.
This suggests an advantageous structuring of the code for the calculation of the gradient and Hessian of 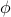 .
.
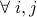
calculate
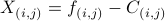 ;
;if (
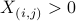 )
)return 0;
if (indicator
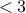 )
)calculate
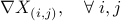 ;
;if (indicator
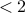 )
)calculate
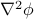 , known as H
, known as H
if (indicator
 or indicator
or indicator 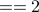 )
)calculate
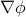 , known as G
, known as G
else
calculate
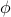 , known as F
, known as F