Lecture 25: Classes & Objects
August 3rd, 2021
Today: JSON, matplotlib (finishing up from lecture 24), classes, and objects
Announcements
- Quiz 2 is on Monday, August 9th starting at 1:30pm PT
- Review materials will come out later today
Object Oriented Programming (OOP)
- There are different paradigms in programming
- So far you have learned imperative programming
-provide a series of direct commands for program execution
-commands are changing the program state
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP)
-define objects that contain data and behavior (functions)
-program is mostly an interaction between objects
-you are calling functions of these objects (called "methods")
- Python allows for programming in either paradigm!
- Other paradigms exist, but we won't talk about those in 106A
Classes and Objects
- What are classes and objects?
- Classes are like blueprints
-They provide a template for a kind of object
-They define a new type
-Ex: "CS106A student" would be a class
-Each of these would have a stanford email, pycharm, a section leader etc.
- Objects are instances of classes
-Can have multiple objects of the same Class type
-Ex: YOU would be an instance of the "CS106A student" Class
-So you have the properties of your Class (CS106A student)
-There are lots of other 106A students out there too
-You are all type "CS106A student"
-You are all objects of the same Class
Example of a Class in Python
Counter Example Zip
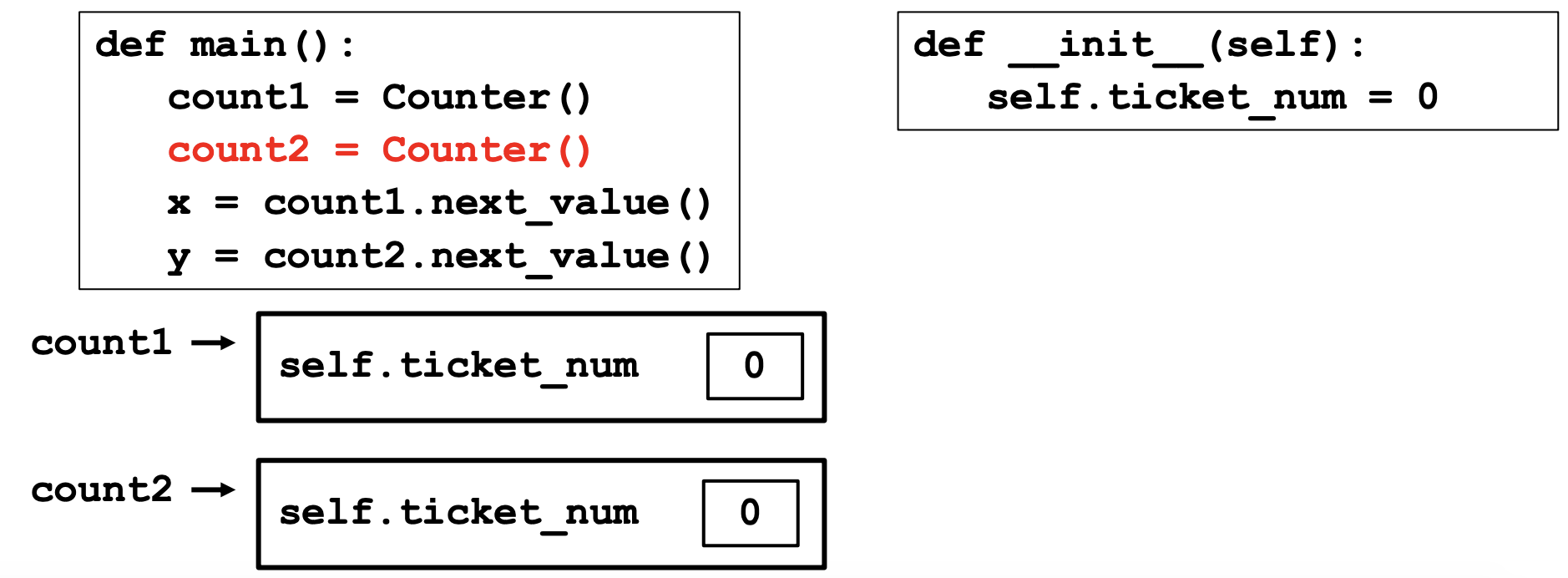
- Counter Class
- Let's create a class that gives people a number representing their spot in line for ice cream
- Want to be able to get a ticket (ask the class for the next ticket number)
- Need to keep track of this next ticket number
- Class names start with Uppercase character (Counter)
- No main() function (a Class is not a program)
- Let's see an example
class Counter:
# Constructor (two underscores - double underscores - known as 'dunder')
def __init__(self):
self.ticket_num = 0 # "instance" variable
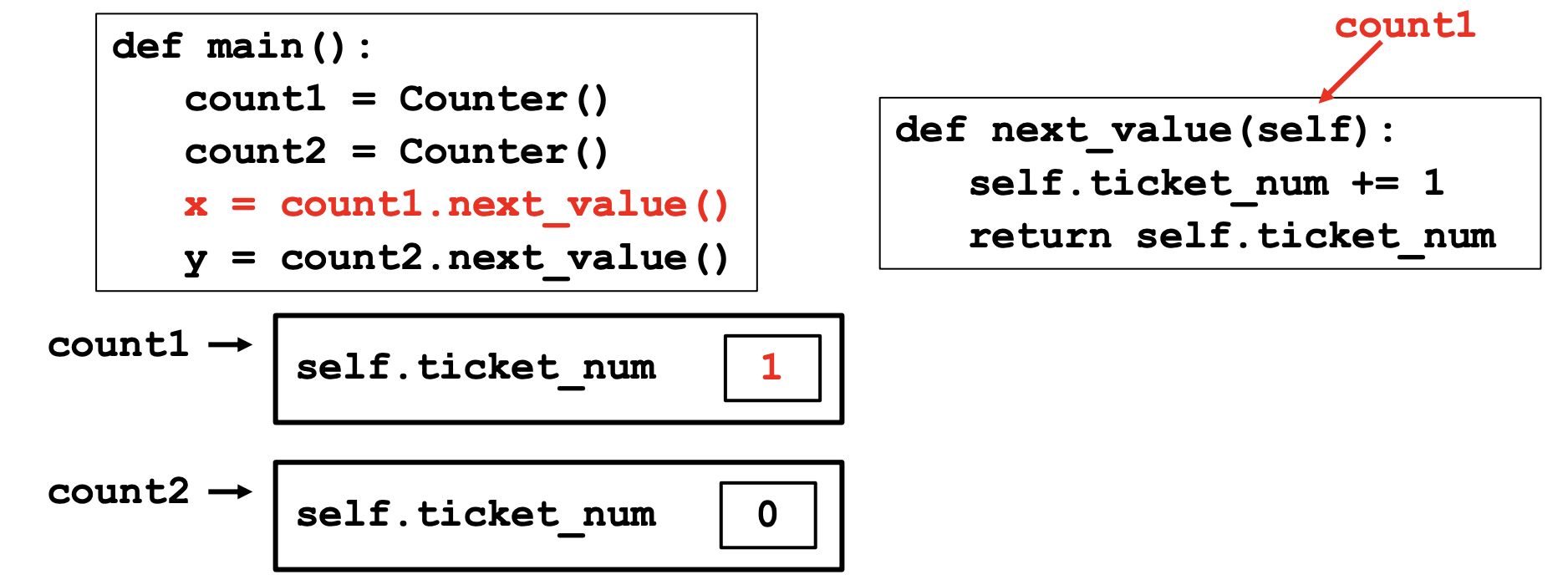
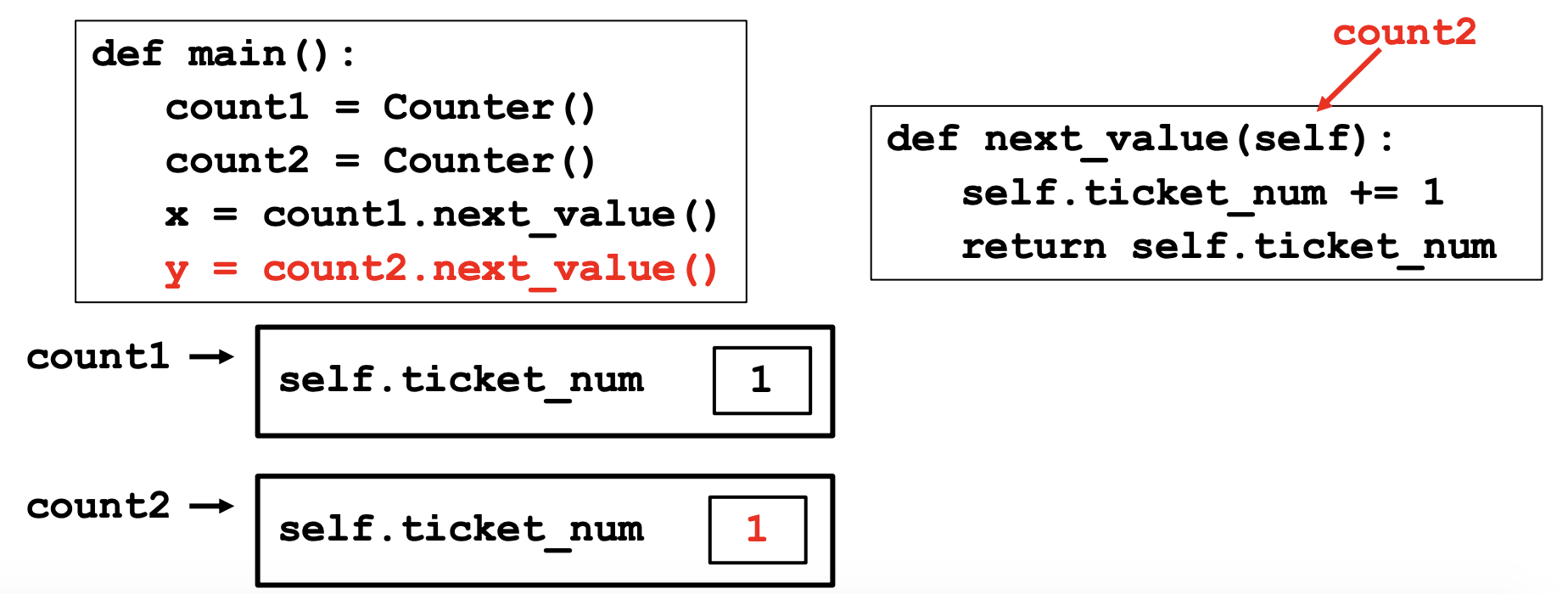
# Method (function) that returns the next ticket value
def next_value(self):
self.ticket_numm += 1
return self.ticket_num
Classes in Action
Objects are Mutable:
- When you pass an object into as a parameter, changes to the object in that function persist after
the function ends
from counter import Counter # import the Class
def count_two_times(counter):
for i in range(2):
print(counter.next_value())
def main():
count1 = Counter()
count2 = Counter()
print('Count1: ')
count_two_times(count1)
print('Count2: ')
count_two_times(count2)
print('Count1: ')
count_two_times(count1)
Output:
Count1:
1
2
Count2:
1
2
Count1:
3
4
How to Write a Class in Python
- Classes are written in their own files
- Filename for the class is usually: classname.py
-Usually the lower case version of the classname in the file (ex: counter.py)
- Let's take a closer look:
class Classname:
# Constructor
def __init__(self, additional parameters):
# body of code
self.variable_name = value # example instance variable
# Method
def method_name(self, additional parameters):
# body of code
Constructor of a Class
- Constructor Syntax
def __init__(self, additional parameters):
# body
- Called when a new object is being created
-Does not explicity specify a return value
-A new object is created and returned
-Can think of a constructor as the factory that creates new objects
-Responsible for intializing objects (setting initial values)
-Generally where instance variables are created (with self)
self.variable_name = value # creates an instance variable
Instance Variables
- Instance variables are variables associated with objects
-Each object gets its own set of instance variables
-Generally, they are initialized in the constructor for the Class
- Instance variables are accessed using
self
self.variable_name = value
self really refers to the specific object that a method is called on
Methods (functions) in a Class
Another Example: Students
Student Class Example Zip
- Want a class to keep track of information for students
- Each student has information:
-Name
-ID number
-Units completed
- Want to specify the name and ID number when creating a student object
-Initially set units completed to 0
-Student's number of units completed can be updated over time
-Also want to be able to check if a student can graduate
Student needs to have at least UNITS_TO_GRADUATE units
- Let's check it out in Pycharm


