Lecture Preview: Sets, Lexicons, and Maps
(Suggested book reading: Programming Abstractions in C++, section 5.4 - 5.6)
In this lecture we will talk about three new data structures:
-
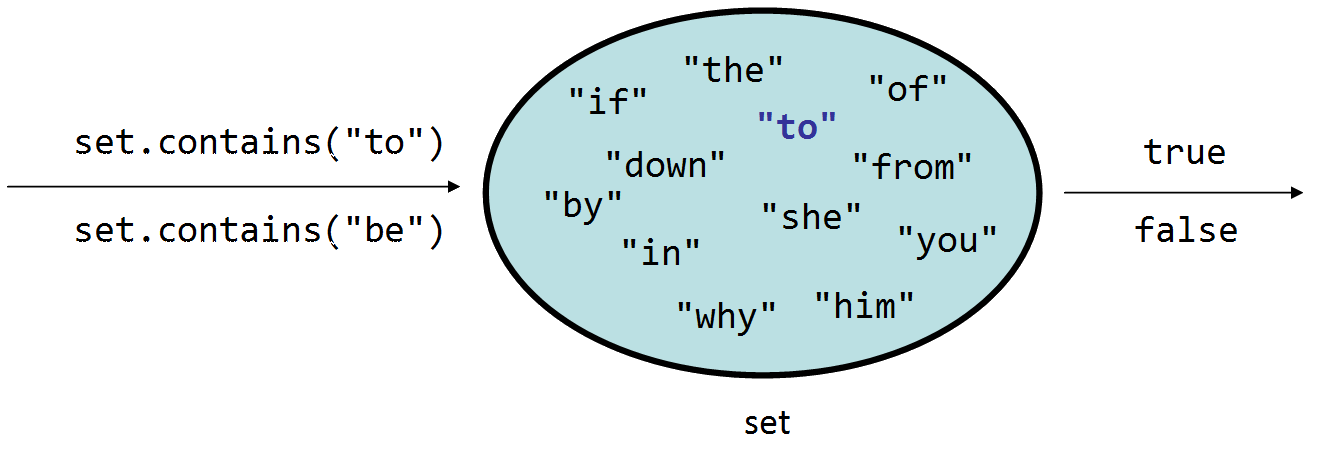
A set is a collection that stores its elements in sorted order and does not allow duplicates. Sets are useful when you want a collection that ensures that all of its data is unique.
-
A lexicon is a set that is specialized to store words from a dictionary. It is good for searching for words or searching for a prefix (starting substring) of a word.
-
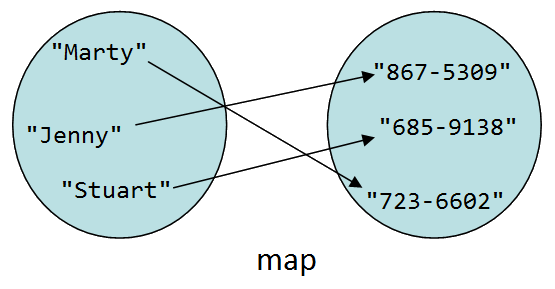
A map is a collection that stores pairs rather than single values. Each pair contains two parts called a key and a value. You can use a key to look up a value later. Maps are useful for storing one-way associations like a dictionary or phone book.
Here is a short code example that uses a set:
Set<int> set; set.add(12); set.add(8); set.add(12); // duplicate; not added set.add(17); set.add(8); // duplicate; not added cout << set << endl; // {8, 12, 17}
Here is a short code example that uses a map:
Map<string, double> salary; salary["Marty"] = 10000.00; // or, salary.put("Marty", 10000.00); salary["Cynthia"] = 40000.00; // or, salary.put("Cynthia", 40000.00); salary["Mehran"] = 2 * salary["Cynthia"]; // or, salary.put("Mehran", 2 * salary.get("Cynthia")); cout << salary << endl; // {"Cynthia":40000.0, "Marty":10000.0, "Mehran":80000.0}
