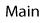Signaling components as Wnt targets
Wnt signaling can promote the expression of several Wnt pathway components, indicating that feedback control is a key feature of Wnt signaling regulation.
The expression of these "Wnt pathway" genes is often more common when different cells exposed to Wnt are compared. Many other Wnt target genes are cell type specific and are less often found to be induced across different kinds of cells. Hence, expression of Wnt pathway genes such as Axin2 and Lgr5 can be a good common hallmark of active Wnt signaling.
Target Gene |
Effect of Wnt signal on target gene expression |
Effect of changes in target gene expression on Wnt pathway |
Target gene interacts with: |
Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Fz |
Down |
Inactivate |
Wnt |
|
|
Dfz2 |
Down |
Inactivate |
Wnt |
|
|
Dfz3 |
Up |
Activate |
Wnt |
|
|
Fz7 |
up |
|
Wnt |
|
|
Arrow/LRP |
Down |
Inactivate |
Wnt |
|
| Dickkopf | Up | Inactivate | LRP | |
|
Dally (HSPG) |
Down |
|
Wnt |
|
|
Wingful/notum |
Up |
Inactivate |
HSPG? |
|
|
naked |
Up |
Inactivate |
Dsh |
|
| nemo | Up | Inactivate | TCF | Zeng , 2004 |
|
Axin2 |
Up |
Inactivate |
β-catenin |
|
|
b-TCRP |
Up |
Inactivate |
β-catenin |
|
|
TCF1 (dn) |
Up |
Inactivate |
TCF |
|
|
LEF1 |
Down |
Activate |
β-catenin |
|
| LGR5 | Up |
|