An experimental approach to measuring DSNU .
The method is described in the paper by Farrell, Feng and Kavusi, 2006, SPIE.
We simulate a large number of short exposure durations to a black scene. We average across the multiple images to eliminate the (presumably unbiased) read noise. We estimate the DSNU as the standard deviation across the pixels.
See also:
Copyright ImagEval Consultants, LLC, 2010.
Contents
ieInit
Make a dark scene, oi and sensor
scene = sceneCreate('uniform ee'); darkScene = sceneAdjustLuminance(scene,0.1); oi = oiCreate('default',[],[],0); % The scene must always be larger than the sensor field of view. sensor = sensorCreate; sensor = sensorSet(sensor,'size',[196 196]); darkScene = sceneSet(darkScene,'fov',sensorGet(sensor,'fov')*1.5); % Compute the dark optical image darkOI = oiCompute(oi,darkScene);
Set sensor parameters
dsnuLevel = 0.05; % Std. dev. of offset in volts prnuLevel = 0.1; % Std. dev of gain, around 1, as a percentage readNoise = 0.001; % Read noise in volts % Set a brief exposure time for DSNU estimation. Because of the short % exposure, the PRNU level is irrelevant. The read noise can matter. If % it is very large, you must average over more trials. expTime = 0.001; % Seconds sensor = sensorSet(sensor,'DSNU level',dsnuLevel); sensor = sensorSet(sensor,'PRNU level',prnuLevel); sensor = sensorSet(sensor,'Exposure Time',expTime); sensor = sensorSet(sensor,'pixel read noise volts', readNoise); % How many color filters? Normally 3 and we use the 2nd one in a Bayer. % But sometimes we might run this script with a monochrome. nFilters = sensorGet(sensor,'nfilters');
Acquire multiple short exposures of the dark image
clear volts % We take the image multiple times so we can average out the read noise nRepeats = 25; nSamp = prod(sensorGet(sensor,'size'))/2; volts = zeros(nSamp,nRepeats); wBar = waitbar(0,'Acquiring images'); showBar = false; for ii=1:nRepeats waitbar(ii/nRepeats,wBar); sensor = sensorCompute(sensor,darkOI,showBar); if nFilters == 3 % Get Green channel volts(:,ii) = sensorGet(sensor,'volts',2); elseif nFilters == 1 % Get the one channel that is there tmp = sensorGet(sensor,'volts'); volts(:,ii) = tmp(:); end end close(wBar); % ieAddObject(sensor); sensorImageWindow;
Estimate the standard deviation across the sensor
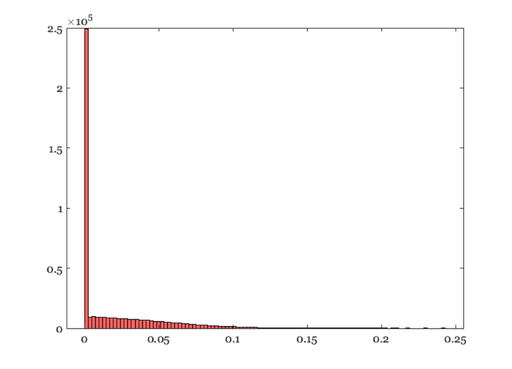
% Notice that the mean offset values for all the pixels are positive (not % zero) because the voltage is forced to be greater than zero at every % pixel. This also reduces the standard deviation and thus the DSNU % estimate, below the true DSNU. vcNewGraphWin; histogram(volts(:),100); % So, get rid of all the very very small, basically zero, voltages v2 = volts(volts > 1e-6); v2 = [-1*v2(:); v2(:)]; fprintf('\n------------\n') fprintf('Estimated standard deviation %.3f vs. simulated DSNU %.3f\n',std(v2(:)),dsnuLevel); fprintf('------------\n')
------------ Estimated standard deviation 0.050 vs. simulated DSNU 0.050 ------------
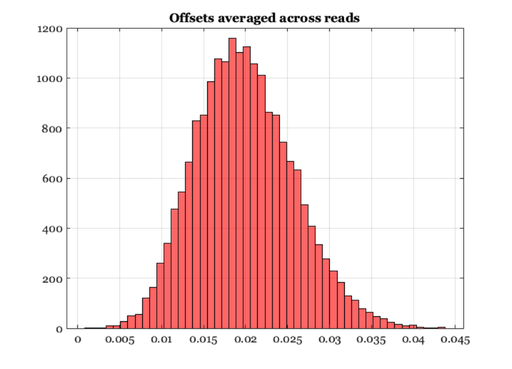
But note that if we simply average across the repeated measures
% We get a number that describes the mean offset for that pixel meanOffset = mean(volts,2); % The histogram is not the DSNU because of the clipping vcNewGraphWin; histogram(meanOffset,50) grid on; title('Offsets averaged across reads');