Creating scene illuminant structures
ISET scenes represent the scene spectral radiance and the scene illuminant. The spectral radiance is a hypercube of data, that is a spectral power distribution (vector) at each scene point.
The simplest illuminant is a single spectral power distribution. In this case the illuminant is constant (the same) at every point in the scene.
Alternatively, the scene illuminant can be a hypercube with the same size as the scene spectral radiance. In that case, we call spatial-spectral . The illuminant is potentially different at every point in the scene.
See also: illuminantCreate, s_sceneIlluminantMixtures, s_sceneIlluminantSpace
(c) Imageval Consulting, LLC 2012
Contents
- Create a blackbody illuminant structure 5000 deg Kelvin
- Create a blackbody illuminant at 3000 deg Kelvin
- D65, 200 cd/m^2
- Equal energy
- Equal photons
- CIE standard illuminant C
- Monochrome at 555 nm
- CIE D65 but sampled over a different wave range
- Interpolate and overlay the two different sampling resolutions
- Fluorescent illuminant
- Tungsten
ieInit
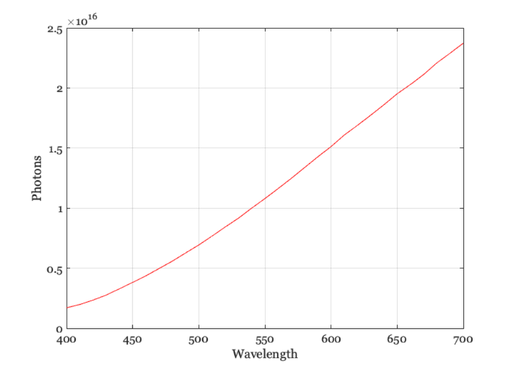
Create a blackbody illuminant structure 5000 deg Kelvin
illum = illuminantCreate('blackbody'); p = illuminantGet(illum,'photons'); w = illuminantGet(illum,'wave'); vcNewGraphWin; plot(w,p); grid on xlabel('Wavelength'); ylabel('Photons')
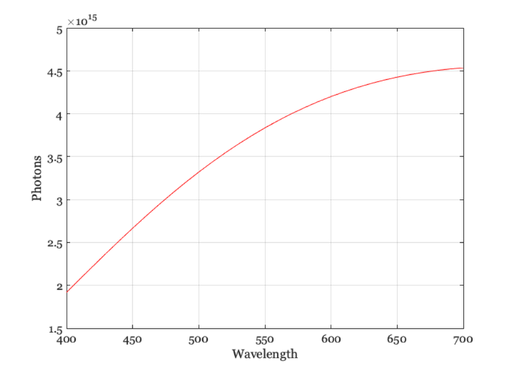
Create a blackbody illuminant at 3000 deg Kelvin
wave = 400:1:700; illum = illuminantCreate('blackbody',wave,3000); p = illuminantGet(illum,'photons'); w = illuminantGet(illum,'wave'); vcNewGraphWin; plot(w,p); grid on xlabel('Wavelength'); ylabel('Photons')
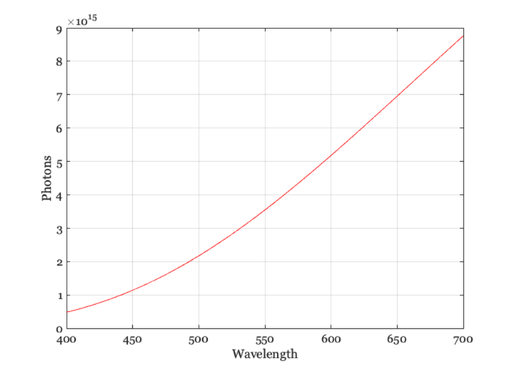
D65, 200 cd/m^2
luminance = 200; wave = []; % Defaults illum = illuminantCreate('d65',wave,luminance); p = illuminantGet(illum,'photons'); w = illuminantGet(illum,'wave'); ieNewGraphWin; plot(w,p); grid on xlabel('Wavelength'); ylabel('Photons')
Equal energy
illum = illuminantCreate('equal energy',[],luminance); e = illuminantGet(illum,'energy'); w = illuminantGet(illum,'wave'); mn = mean(e(:)); vcNewGraphWin; plot(w,e); grid on xlabel('Wavelength'); ylabel('Energy') set(gca,'ylim',[0.9*mn,1.1*mn]);
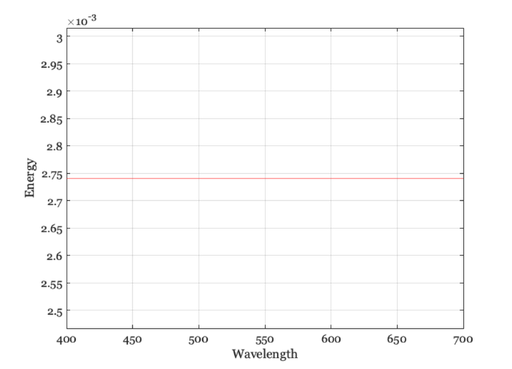
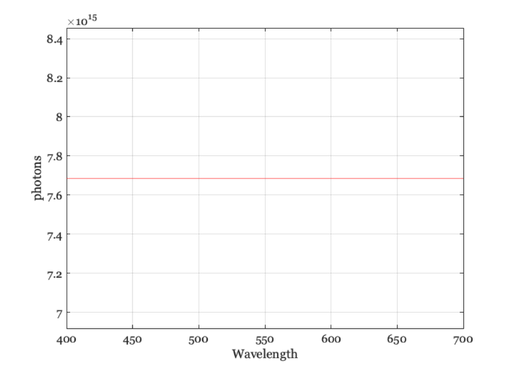
Equal photons
illum = illuminantCreate('equal photons',[],luminance); p = illuminantGet(illum,'photons'); e = illuminantGet(illum,'energy'); w = illuminantGet(illum,'wave'); vcNewGraphWin; plot(w,p); grid on xlabel('Wavelength'); ylabel('photons') mn = mean(p(:)); set(gca,'ylim',[0.9*mn,1.1*mn]); vcNewGraphWin; plot(w,e); grid on xlabel('Wavelength'); ylabel('Energy')

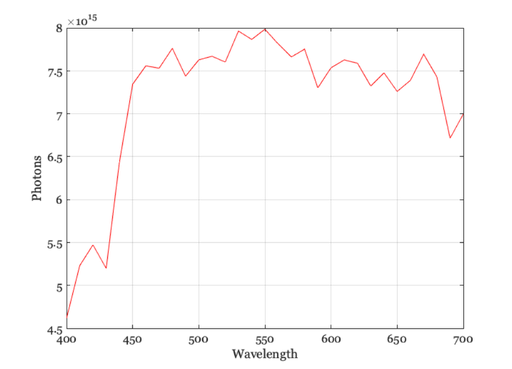
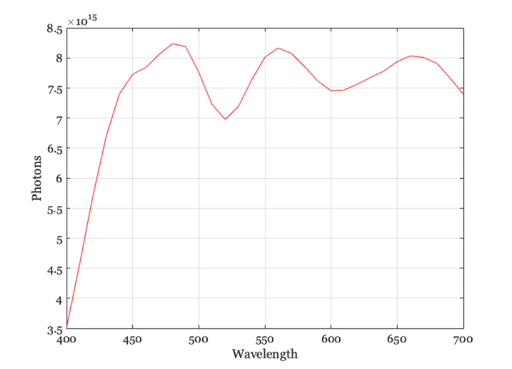
CIE standard illuminant C
illum = illuminantCreate('illuminant C',[],luminance); p = illuminantGet(illum,'photons'); w = illuminantGet(illum,'wave'); vcNewGraphWin; plot(w,p); grid on xlabel('Wavelength'); ylabel('Photons')
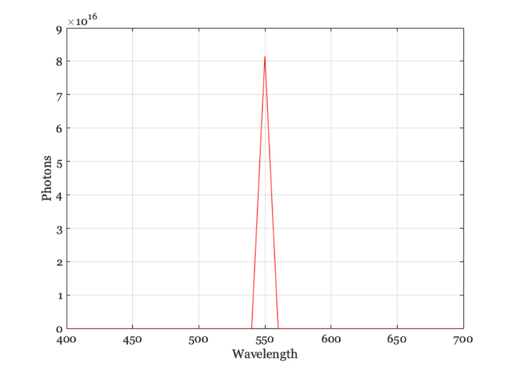
Monochrome at 555 nm
illum = illuminantCreate('555 nm',[],luminance); p = illuminantGet(illum,'photons'); w = illuminantGet(illum,'wave'); vcNewGraphWin; plot(w,p); grid on xlabel('Wavelength'); ylabel('Photons')
CIE D65 but sampled over a different wave range
illum = illuminantCreate('d65',400:2:600,200); e = illuminantGet(illum,'energy'); w = illuminantGet(illum,'wave'); vcNewGraphWin([]); plot(w,e,'ks-'); grid on xlabel('Wavelength'); ylabel('Energy')
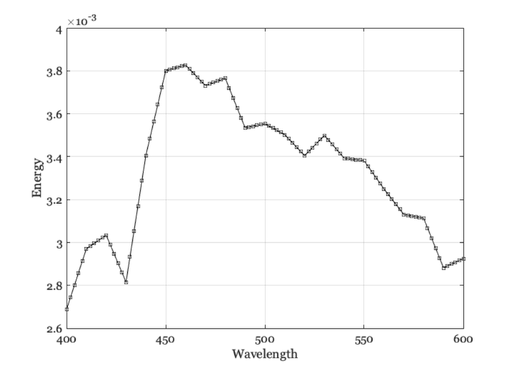
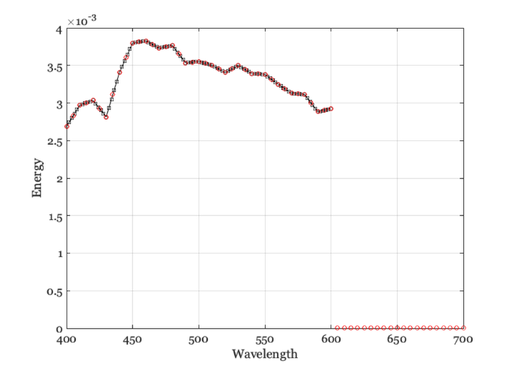
Interpolate and overlay the two different sampling resolutions
illum2 = illuminantSet(illum,'wave',400:5:700); e = illuminantGet(illum2,'energy'); w = illuminantGet(illum2,'wave'); hold on; plot(w,e,'ro'); grid on xlabel('Wavelength'); ylabel('Energy')
Fluorescent illuminant
illum = illuminantCreate('fluorescent',400:5:700,10); p = illuminantGet(illum,'photons'); w = illuminantGet(illum,'wave'); vcNewGraphWin; plot(w,p); grid on xlabel('Wavelength'); ylabel('Photons')

Tungsten
illum = illuminantCreate('tungsten',[],300); p = illuminantGet(illum,'photons'); w = illuminantGet(illum,'wave'); vcNewGraphWin; plot(w,p); grid on xlabel('Wavelength'); ylabel('Photons')