Illustrate how to control of the image processing routines
Illuminant correction and demosaicking are illustrated.
Copyright ImagEval Consultants, LLC, 2007.
Contents
- First, create a simple colorful test scene
- We are ready to create and experiment with the image processing calls.
- Set the sensor correction parameters
- Set the illuminant correction algorithm
- Now, illustrate a different demosaic algorithm
- How the sensor conversion matrix is calculated
- Interacting with the image processing display
- This is an image the display gamut in chromaticity coordinates
- The display volume in Lab space
- Display subpixel pointspreads
- END
ieInit
First, create a simple colorful test scene
scene = sceneCreate('macbeth tungsten'); oi = oiCreate; sensor = sensorCreate; sensor = sensorSet(sensor,'size',[340 420]); % Match the scene field of view to the sensor size fov = sensorGet(sensor,'fov',sceneGet(scene,'distance'),oi); scene = sceneSet(scene,'fov',fov); % Compute the optical image and sensor from the scene. oi = oiCompute(oi,scene); sensor = sensorCompute(sensor,oi); ieAddObject(sensor);
We are ready to create and experiment with the image processing calls.
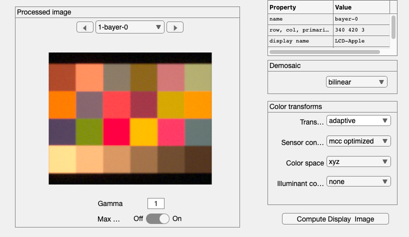
% Create the image processor. ip = ipCreate; ip = ipSet(ip,'name','default'); % First, we compute using the default image processing pipeline. % Reading the boxes on the right of the window, we see the default % processing steps. These are % % * Bilinear demosaicking % * Converting the sensor data into a calibrated internal color space % * Correcting for the illumination % % The demosaicking algorithm is implemented in Demosaic.m % The sensor conversion in the default uses this logic: % * We know the sensor spectral responsivities % * We find the 3x3 linear transformation that best maps (least-squares) % the sensor values into a calibrated color space (See notes below). %
Set the sensor correction parameters
% Choose the internal color space ip = ipSet(ip,'internal cs','XYZ'); % Choose the likely set of signals the sensor will encounter ip = ipSet(ip,'conversion method sensor','MCC Optimized'); % Give the image processor a name ip = ipSet(ip,'name','MCC-XYZ'); % Note that at this point we have left illuminant correction to 'None'. So % there will be no illuminant correction at this point. % Compute from sensor to sRGB ip = ipCompute(ip,sensor); ipWindow(ip);
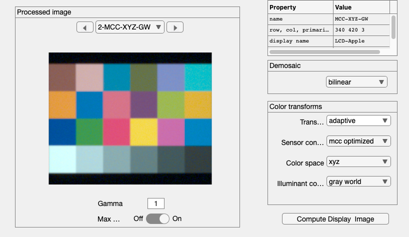
Set the illuminant correction algorithm
% We have only three default options at this point. ip = ipSet(ip,'illuminant correction method','gray world'); ip = ipCompute(ip,sensor); ip = ipSet(ip,'name','MCC-XYZ-GW'); ieAddObject(ip); ipWindow;
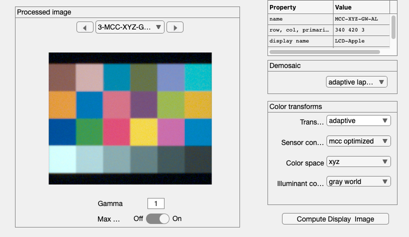
Now, illustrate a different demosaic algorithm
ip = ipSet(ip,'demosaic method','Adaptive Laplacian'); ip = ipCompute(ip,sensor); ip = ipSet(ip,'name','MCC-XYZ-GW-AL'); ieAddObject(ip); ipWindow;
How the sensor conversion matrix is calculated
The transformation is calculated by predicting the sensor responses to a MCC under D65 and then finding the 3x3 matrix that maps the sensor values into the correct MCC values for a D65 light
Interacting with the image processing display
% This is the display structure d = ipGet(ip,'display'); disp(d) % There is a separate window for interacting with the display % See t_displayIntroduction.
type: 'display'
name: 'LCD-Apple'
wave: [31×1 double]
spd: [31×3 double]
gamma: [1024×3 double]
dpi: 96
dist: 0.5000
isEmissive: 1
dixel: [1×1 struct]
ambient: [31×1 double]
image: []
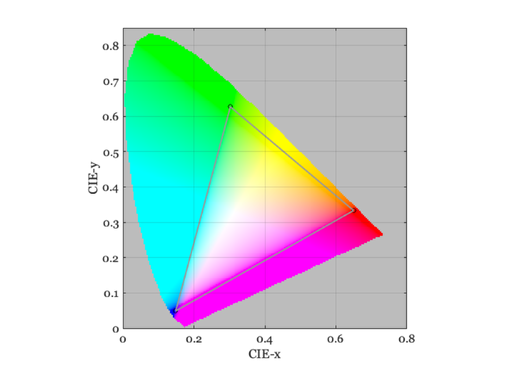
This is an image the display gamut in chromaticity coordinates
displayPlot(d,'gamut');
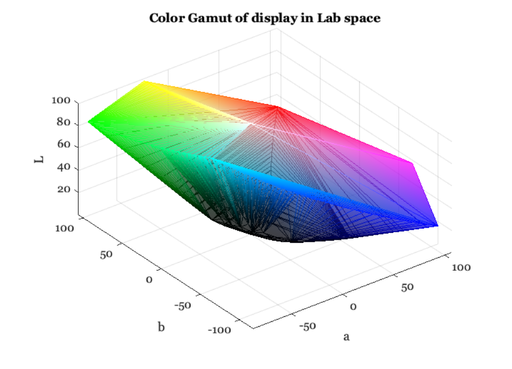
The display volume in Lab space
displayPlot(d,'gamut 3d');
Display subpixel pointspreads
displayPlot(d,'psf')