Semi-automatic artifact removal tool (smart)

SMART was developed during my dissertation work at the University of Texas at Austin. The idea was to preprocess electroencephalogram (EEG) data that was collected while participants meditated with their eyes closed. EEG is infamous for getting easily corrupted by muscular and other artifactual sources of noise. Thus, we used a two step process of pre-processing EEG data. First, we used second-order blind source separation to find sources that were uncorrelated in time (hence second-order). Second, we developed a novel semi-automatic web-based tool (or SMART) to identify non-neural sources of artifact (e.g., muscular artifact, ocular artifact, and interference by power lines).
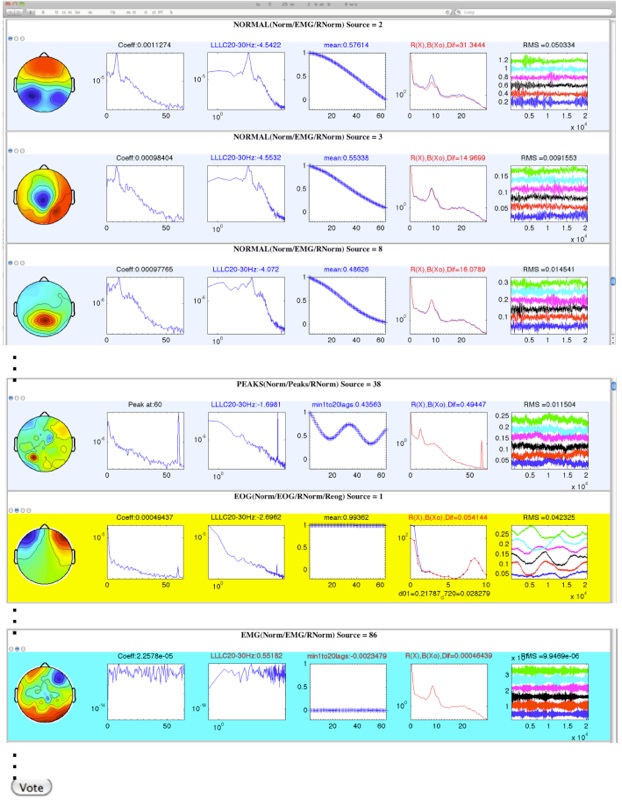
The identification of artifacts was done in SMART by using three key pieces of information - topological, temporal (mainly auto-correlation function), and spectral structure of each component. Based on simple rules, first SMART identified sources as different kinds of artifacts. Followed by generating a web-based tool, so that the researcher can quickly and efficiently go over all the components and their corresponding properties to judge whether SMART correctly classified the source under consideration as noise or not. If not, then the researcher can override source’s classification by clicking a radio button. The screenshot below better portrays the point.
The source code is provided at the end of this page. For more information on the SMART tool, please see the following references. Also, if you use this tool in your research, please cite these as well.
-
(1)Saggar M, et al. (2012) Intensive training induces longitudinal changes in meditation state-related EEG oscillatory activity. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 6:256. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2012.00256
-
(2)Saggar, M. (2011) Computational analysis of meditation. Retrieved from University of Texas Digital Repository: Electronic Theses and Dissertations, (Austin, TX), Pages: 24-44.
NOTE: SMART for other imaging modalities (fMRI and fNIRS) is under testing and will be released very soon.
Screenshot of SMART:

Source code for SMART:
Copyright (C) 2011 Manish Saggar
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
This software contains three source files (two written in Matlab and one in Perl). Click here to download the zip file.
NOTE: Any blind source separation algorithm can be used with SMART. In my dissertation I used the second-order blind source separation (SOBI) algorithm. See following papers for more information on how to use SOBI with EEG data. One example implementation is also provided in the EEGLab toolkit.
-
(1)Akaysha C. Tang, Matthew T. Sutherland, Christopher J. McKinney. Validation of SOBI components from high-density EEG. NeuroImage, Volume 25, Issue 2, 1 April 2005, Pages 539–553
-
(2)Akaysha C. Tang, Jing-Yu Liu, Matthew T. Sutherland. Recovery of correlated neuronal sources from EEG: The good and bad ways of using SOBI. NeuroImage, Volume 28, Issue 2, 1 November 2005, Pages 507–519