Compressed Sensing Based Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Reconstruction with a First-Order Method
Medical Physics, 37(9):5113–5125, September 2010.
This article considers the problem of reconstructing cone-beam
computed tomography (CBCT) images from a set of undersampled and potentially
noisy projection measurements. The authors cast the reconstruction as
a compressed sensing problem based on 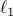 norm minimization constrained by
statistically weighted least-squares of CBCT projection data. For accurate
modeling, the noise characteristics of the CBCT projection data are used to
determine the relative importance of each projection measurement. To solve the
compressed sensing problem, the authors employ a method minimizing
total-variation norm, satisfying a prespecified level of measurement
consistency using a first-order method developed by Nesterov. The
method converges fast to the optimal solution without excessive memory
requirement, thanks to the method of iterative forward and back-projections.
The performance of the proposed algorithm is demonstrated through a series of
digital and experimental phantom studies. It is found a that high quality CBCT
image can be reconstructed from undersampled and potentially noisy projection
data by using the proposed method. Both sparse sampling and decreasing x-ray
tube current (i.e., noisy projection data) lead to the reduction of radiation
dose in CBCT imaging. It is demonstrated that compressed sensing
outperforms the traditional algorithm when dealing with sparse, and potentially
noisy, CBCT projection views.
norm minimization constrained by
statistically weighted least-squares of CBCT projection data. For accurate
modeling, the noise characteristics of the CBCT projection data are used to
determine the relative importance of each projection measurement. To solve the
compressed sensing problem, the authors employ a method minimizing
total-variation norm, satisfying a prespecified level of measurement
consistency using a first-order method developed by Nesterov. The
method converges fast to the optimal solution without excessive memory
requirement, thanks to the method of iterative forward and back-projections.
The performance of the proposed algorithm is demonstrated through a series of
digital and experimental phantom studies. It is found a that high quality CBCT
image can be reconstructed from undersampled and potentially noisy projection
data by using the proposed method. Both sparse sampling and decreasing x-ray
tube current (i.e., noisy projection data) lead to the reduction of radiation
dose in CBCT imaging. It is demonstrated that compressed sensing
outperforms the traditional algorithm when dealing with sparse, and potentially
noisy, CBCT projection views.