Stanford, Winter 2023-24

# CS106A Exam Reference Reminder
# [square brackets] denote functions listed here that we have not used yet
# Exam questions will not depend on functions we have not used yet
Bit:
bit = Bit(filename)
bit.front_clear() bit.left_clear() bit.right_clear()
bit.get_color()
bit.move() bit.left() bit.right()
bit.paint('red') [bit.erase()]
General functions:
len() int() str() range() [list() sorted()]
String functions:
isalpha() isdigit() isspace() isupper() islower()
find() upper() lower() strip()
List functions:
append() index() [extend() pop() insert()]
SimpleImage:
# read filename
image = SimpleImage(filename)
# create blank image
image = SimpleImage.blank(width, height)
# foreach loop
for pixel in image:
# range/y/x loop
for y in range(image.height):
for x in range(image.width):
pixel = image.get_pixel(x, y)
Grid 2D:
grid = Grid.build([['row', '0'], ['row', '1']])
grid.width, grid.height - properties
grid.in_bounds(x, y) - True if in bounds
grid.get(x, y) - returns contents at that x,y, or None if empty
grid.set(x, y, value) - sets new value into grid at x,y
a. By each ???, write what value comes from the Python expression:
>>> 10 - 2 * 3 - 2 + 1 ??? >>> 52 % 10 ??? >>> s = 'Python' >>> s[:3] ??? >>> s[3:] ???
b. What 3 numbers print when the caller() function runs? This code runs without error.
def foo(a, b):
a = 2 * a
b = 2
return a + b
def caller():
a = 2
b = 3
c = foo(b, 1)
print(a, b, c)
# What 3 numbers print ???
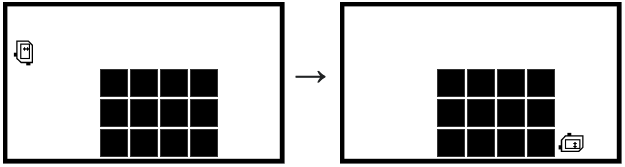
Bit is facing the right side of the world. Below bit is empty space. Move bit forward 1 or more squares until solid ground appears below. This is the top of a flat mesa. Move bit forward across the top of the mesa until empty space appears below. Turn bit to face the bottom of the world. Move bit forward until blocked.
Bit before and after:
def do_mesa(filename):
bit = Bit(filename)
# Your code here
Given an image filename and ints a and b which are 1 or more.
Produce a new out image with three features: (1) a blank rectangle a pixels high and the same width as the original image at the upper left of the output image. (2) a horizontally flipped copy of the original image immediately below the blank rectangle. (3) To the right of the rectangle and image, a vertical aqua stripe b pixels wide, running down the height of the output image. Please try to avoid writing too close to the right edge of the paper.
1. Write one line of code to create the out image.
2. Almost all of the code to write the flipped image is provided — looping over the original image, writing the colors at each "pixel" to "pixel_out". Write the one line of code which sets the "pixel_out" variable used by the later lines in this loop. It's ok if you need to put the parameters on multiple lines to make it fit.
3. Write the loops and other needed code to produce the aqua stripe at the right side. These are separate loops, not nested inside the earlier loops. You can change a white pixel to aqua by setting its red value to 0. We'll assume there is a return out as the last line.
def do_image(filename, a, b):
image = SimpleImage(filename)
#### 1. Create "out" image
# Write flipped image to out
for y in range(image.height):
for x in range(image.width):
pixel = image.get_pixel(x, y)
#### 2. Set "pixel_out"
pixel_out.red = pixel.red
pixel_out.green = pixel.green
pixel_out.blue = pixel.blue
#### 3. Fill aqua rectangle
a. Given a string s, return a string such that: for every alphabetic char in s, the result has 2 copies of that char. Omit non-alphabetic chars.
'#abc6' -> 'aabbcc' | def double_alpha(s): 'Yo' -> 'YYoo' | ',,X,Y' -> 'XXYY' |
b. Given a string s. Find the first dot '.' in s. If there is a digit immediately before the '.', such as the '1' in 'x1.c24z', call that the first digit. Look for a second digit exactly 3 chars after the dot, such as the '4' in 'x1.c24z'. If the first and second digits are both present, return their arithmetic sum. If only the dot and first digit are present, return the first digit's value squared. If there is no dot or no first digit, return -1.
'x1.c246z' -> 5 | def digit_dot(s): 'ab12.cc71cc' -> 9 | 'x1.aa91b' -> 10 | 'abc9.zz5' -> 14 | 'a23.zzz' -> 9 'bb5.zz' -> 25 'aa.zzz' -> -1 '.' -> -1 'zzz' -> -1
c. Given a string s, find the first '^^^^' in s. Then find the first '^^' that comes after the '^^^^', returning None if either is not found. For an input like 'xx^^^^aaaa^^bb' return 'bbaaaa'. That is, return a string made of the chars after the '^^' followed by the chars between the '^^^^'and the '^^'. Use s.find() and slices.
'xx^^^^aaaa^^bb' | def hat_str(s): -> 'bbaaaa' | 'xx^^^^ it^^so be' | -> 'so be it' | '^^^^1^^2' -> '21' | '^^^^xyz' -> None 'nopexyz' -> None
In this problem, every square is one of these four values: empty None, squirrel 's', apple 'a', or banana 'b'. The 'a' and 'b' are the "food" squares. As usual, you can get full credit for each part independently of what you write on the other parts.
a. Write a helper function same_food(s1, s2) that takes 2 values representing grid contents. The s1 and s2 parameters will always be drawn from the four values: None, 's', 'a', 'b'. Return True if both s1 and s2 are 'a', or they are both 'b', i.e. s1 and s2 are the same food. In all other cases, return False. Here are example cases expressed as Doctests:
>>> same_food('a', 'a')
True
>>> same_food('b', 'b')
True
>>> same_food('a', 'b')
False
>>> same_food(None, None)
False
>>> same_food('s', 's')
False
def same_food(s1, s2):
(b) The function de_squirrel(grid, x, y, n) will be called with an in-bounds x, y. This function will attempt a "de-squirrel" action to make a squirrel disappear. Write code for the de-squirrel action with these steps:
1. There must be a squirrel at x, y for the action to proceed.
2. Consider the 2 squares: (1) the square immediately above the squirrel, and (2) the square 1 column to the right and exactly n squares below the squirrel. The parameter n will be an int, 1 or greater.
3. Call the helper from part (a) to check if the two squares identified in the previous step contain the same food. If so, change the square containing the squirrel to None so the squirrel disappears, and return the changed grid. The foods are not removed.
4. In all other cases, leave the grid unchanged and return it.
def de_squirrel(grid, x, y, n):
(c) Add the two lines to complete the following Doctest for a call to de_squirrel() where the de-squirrel action succeeds and the squirrel disappears. The first Grid.build() line is provided which builds a small grid suitable for this Doctest.
>>> grid = Grid.build([['a', None], ['s', None], [None, 'a']]) >>>
This problem uses an encryption scheme somewhat like the homework. As a simplification, assume the char to encrypt is not uppercase. The encryption uses a source list of lowercase chars, a slug list with both lowercase chars and digits, and an additional "digital" list of lowercase chars. The source and slug lists are the same length. (The example lists below show just 4 source chars as a simplification):
source = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'] slug = ['d', '2', 'b', '0'] digital = ['k', 'm', 'e', 'w'] indexes 0 1 2 3
Write code to encrypt an input char with the following algorithm:
1. If the input ch is not in the source list, its encrypted form is simply the char itself, e.g. '$' -> '$'
2. As on the homework, consider the index of the input ch in the source list, and the slug char at the same index. For example, for input ch 'a', the index is 0, and the slug char is 'd'.
3. If the slug char is a digit, e.g. '2', the encrypted form is the char at that digit index in the digital list. For example, for the input 'b', the slug char is '2', so the encrypted form is at index 2 in the digital list, e.g. 'e'. The digital list is guaranteed to be sufficient length to support all the digit chars which appear in the slug list. Note that the elements in all the lists are strings.
4. Otherwise, if the slug char is not a digit, the slug char itself is the encrypted form.
Encryption examples 'a' -> 'd' 'b' -> 'e' (via '2') 'c' -> 'b' 'd' -> 'k' (via '0') '$' -> '$"
def encrypt_char(source, slug, digital, ch):
# Your code here
### 1 Short Answer
3
2
Pyt
hon
Function call:
2 3 8
### 2 Bit
def do_mesa(filename):
bit = Bit(filename)
# Move to mesa top
while bit.right_clear():
bit.move()
# Move across the top
while not bit.right_clear():
bit.move()
# Down to the bottom
bit.right()
while bit.front_clear():
bit.move()
### 3 Image
out = SimpleImage.blank(image.width + b, image.height + a)
pixel_out = out.get_pixel(image.width - 1 - x, y + a)
# or equivalently
pixel_out = out.get_pixel(out.width - b - 1 - x, y + a)
for y in range(image.height + a) # or out.height
for x in range(b):
# Need to shift over by image.width
out_pix = out.get_pixel(image.width + x, y)
out_pix.red = 0
### 4 Strings
def double_alpha(s):
result = ''
for ch in s: # or for/i/range
if ch.isalpha():
result += ch + ch
return result
def digit_dot(s):
dot = s.find('.')
# Screen out bad-dot cases
if dot == -1 or dot == 0: # dot == 0 -> no char to its left
return -1
if s[dot - 1].isdigit():
# Second digit? make sum of both digits
if dot + 3 < len(s) and s[dot + 3].isdigit():
return int(s[dot - 1]) + int(s[dot + 3])
# Otherwise first digit squared
return int(s[dot - 1]) * int(s[dot - 1])
return -1
def hat_str(s):
first = s.find('^^^^')
second = s.find('^^', first + 4) # Search after first
if first == -1 or second == -1:
return None
return s[second + 2:] + s[first + 4:second]
### 5 Grid
def same_food(s1, s2):
# v1 - maybe the most straightforward
if s1 == 'a' and s2 == 'a':
return True
if s1 == 'b' and s2 == 'b':
return True
return False
# v2 shorter
if s1 == s2 and (s1 == 'a' or s1 == 'b'):
return True
return False
# v3 "or" detect the ways it can be False
if s1 != s2 or s1 == None or s1 == 's':
return False
return True
def de_squirrel(grid, x, y, n):
if grid.get(x, y) != 's':
return grid
if grid.in_bounds(x, y - 1) and grid.in_bounds(x + 1, y + n):
# Not required, but putting grid contents in vars
s1 = grid.get(x, y - 1) # above squirrel
s2 = grid.get(x + 1, y + n) # to the right and below
if same_food(s1, s2):
grid.set(x, y, None)
return grid
# Doctest
>>> grid = Grid.build([['a', None], ['s', None], [None, 'a']])
>>> de_squirrel(grid, 0, 1, 1)
[['a', None], [None, None], [None, 'a']]
### 6 Cryptography
def encrypt(source, slug, digital, ch)"
if ch in source:
# Find slug char at same index
idx = source.index(ch)
crypt = slug[idx]
# What if it's a digit?
if crypt.isdigit():
num = int(crypt)
return digital[num]
return crypt
return ch