Exam instructions: There are 5 questions. Write all answers directly on the exam. This printed exam is closed-book and closed-device; you may refer only to your one letter-sized page of prepared notes and the provided reference sheet. You have 2 hours to complete the exam.
C++ coding guidelines: Unless otherwise restricted in the instructions for a specific problem, you
are free to use any of the CS106 libraries and classes we've covered in class. You don't need #include statements in your
solutions, just assume the required vector, strlib, etc. header files are visible. You do not need
to declare prototypes. You are free to create helper functions unless the problem states otherwise.
Comments are not required, but when your code is incorrect, comments could clarify your
intentions and help earn partial credit.
Q1) C++ Fundamentals
The seating chart for an airplane is stored in a Grid<string>. Each grid element is the group
reservation code if that seat is assigned or an empty string if the seat is unoccupied. The diagram
below is a seat grid of 3 rows and 6 columns. Of the 18 total seats, 11 are reserved and 7 are empty.
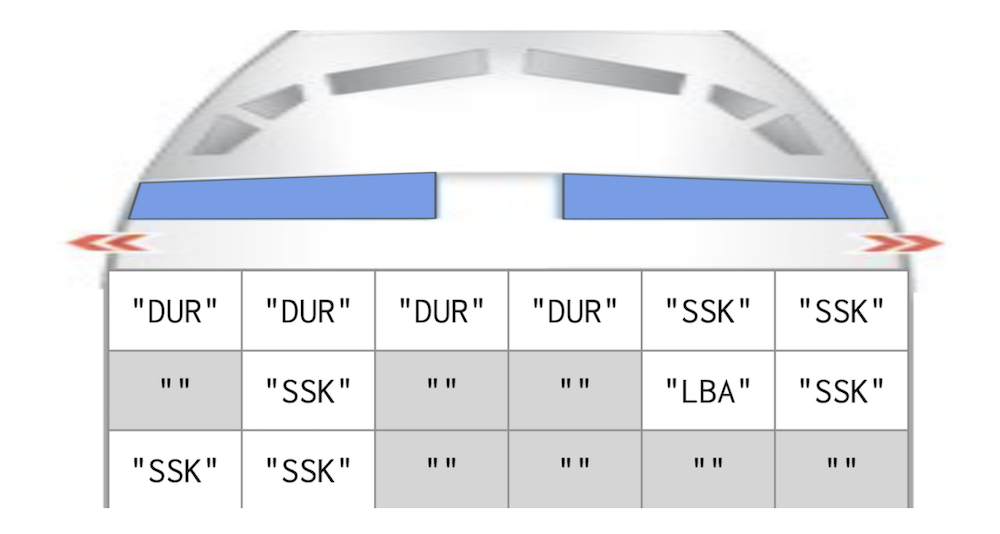
A free block is a sequence of 1 or more adjacent empty seats within a row. In the diagram above:
- row 0 has no free block
- row 1 has two free blocks, a block of size 1 starting at location
{1, 0}and a block of size 2 starting at location{1, 2} - row 2 has a free block of size 4 starting at location
{2, 2}
Write the function findFreeBlock that searches seatGrid for a free block of at least size k.
bool findFreeBlock(Grid<string>& seatGrid, int k, GridLocation& loc)
The function has three parameters:
seatGrid, aGrid<string>as described above.k, the size of the free block to find. You may assume thatk > 0.loc, aGridLocationpassed by reference. –locis assigned to the start location of the free block if one is found. If there is more than one free block of the requested size, it may choose any of them. – If there is no such free block,locis unchanged.
The function returns true if a free block was found and false otherwise.
If seatGrid is the diagram above:
findFreeBlock(seatGrid, 5, loc)returnsfalse,locis unchanged.findFreeBlock(seatGrid, 3, loc)returnstrue,locis either{2, 2}or{2, 3}.
Your code here:
bool findFreeBlock(Grid<string>& seatGrid, int k, GridLocation& loc)
Q2) ADTS
Note: This question builds on the airplane seatGrid introduced in the previous question.
You are given the helper function getSeatsForBlock that returns a set of locations for the block
of k seats starting at location loc:
Set<GridLocation> getSeatsForBlock(GridLocation loc, int k) {
Set<GridLocation> seats;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
GridLocation next = {loc.row, loc.col + i};
seats.add(next);
}
return seats;
}
The call getSeatsForBlock({1, 2}, 2) returns the set of locations { {1, 2}, {1, 3} }. You
will use this helper when implementing the reseatGroup operation.
In addition to the seatGrid previously described, the airline also maintains a reservationDB of
type Map<string, Set<GridLocation>>. In the map, each key is a group reservation code and
associated value is the set of seat locations assigned to the group. Here is the reservationDB that
corresponds to the seatGrid diagram shown in Problem 1.
Key Value
---------------------------------
"DUR" -> { {0,0}, {0,1}, {0,2}, {0,3} }
"LBA" -> { {1,4} }
"SSK" -> { {0,4}, {0,5}, {1,1}, {1,5}, {2,0}, {2,1} }
The group “SSK” has been assigned non-adjacent seats. Write the function reseatGroup that
attempts to reassign the entire group to adjacent seats in a single row.
int reseatGroup(Grid<string>& seatGrid,
Map<string, Set<GridLocation>>& reservationDB,
string groupCode)
The function has three parameters:
seatGrid, aGrid<string>representing the airplane seat gridreservationDB, aMap<string, Set<GridLocation>>of reservationsgroupCode, the group reservation code of the group to reseat. You may assume the group has an entry inreservationDBand seat assignments inseatGrid.
To reseat the group, the function follows these steps:
- Edit
seatGridto release the original seat assignments for the group. - Find a free block of adjacent empty seats. You should call
findFreeBlockandgetSeatsForBlockand may assume they work correctly. - If a free block is found, assign that block of seats to the group and update both
seatGridandreservationsDBto reflect the new seat assignments. - If no reseating was possible, restore the group to their original seat assignments.
- The group reservation code stays the same whether or not the group is reseated.
The function returns the count of seat changes. If reseated, this is the number of different seats between the original and new seat assignments, or zero if no seat assignments were changed.
If seatGrid is the diagram on page 2, reseatGroup(seatGrid, reservationDB, "SSK") reassigns the "SSK" group to the six seats in row 2 and return 4.
Your code here:
int reseatGroup(Grid<string>& seatGrid,
Map<string, Set<GridLocation>>& reservationDB,
string groupCode)
Q3) Code study: ADTs and Big-O
The expunge operation modifies a collection by removing its first element and any duplicates of that value. You will study three versions of expunge, one each for a Vector, Queue, Stack.
The expungeVector function removes a vector's first (index 0) element and all duplicates. This
code has been tested and shown to work correctly on all inputs.
void expungeVector(Vector<int>& vec) {
if (!vec.isEmpty()) {
int first = vec[0];
for (int i = vec.size()-1; i >= 0; i--) { // line 13
int cur = vec[i];
if (cur == first) {
vec.remove(i);
}
}
}
}
a) What is the Big-O runtime of expungeVector when running on a Vector of size N where every
third element is a duplicate of the first element?
Your answer here:
Here are some of the test cases that were used to confirm the correctness of expungeVector:
Input vector Expected result Actual result
-------------------------------------------------
{} {} {}
{4, 1, 7} {1, 7} {1, 7}
{4, 1, 4, 8} {1, 8} {1, 8}
The original code had no comment to provide a rationale for why the loop runs backwards. You change line 13 to iterate over the same indexes in forward order instead. Below is the edited code:
void expungeVector(Vector<int>& vec) {
if (!vec.isEmpty()) {
int first = vec[0];
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) { // changed line 13
int cur = vec[i];
if (cur == first) {
vec.remove(i);
}
}
}
}
b) Give an example test case (input, expected, actual) that would have worked correctly for the original code that will now fail after your edits.
Your test case here:
The expungeQueue function intends to remove the queue's first (frontmost) element and all
duplicates. It may or may not work as intended on all inputs.
void expungeQueue(Queue<int>& queue) {
if (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int first = queue.peek();
for (int i = queue.size()-1; i >= 0; i--) {
int cur = queue.dequeue();
if (cur != first) {
queue.enqueue(cur);
}
}
}
}
c) What is the Big-O runtime of expungeQueue when running on a Queue of size N that contains
no duplicate elements?
Your answer here:
You create the test cases below to test expungeQueue on inputs where the queue's frontmost
element is not duplicated elsewhere in the queue. expungeQueue works correctly on both test
cases. (Note: when listing queue elements, the order is frontmost to lastmost.)
Input queue Expected result Actual result
-------------------------------------------------
{} {} {}
{4, 1, 7} {1, 7} {1, 7}
You now move on to writing test cases when the frontmost element is duplicated.
d) Give an example test case in which the frontmost element is duplicated for
which expungeQueue works correctly (or write None if there is no such input).
Your test case here:
e) Give an example test case in which the frontmost element is duplicated for
which expungeQueue does not work correctly (or write None if there is no such input).
Your test case here:
The expungeStack function intends to remove the stack's first (topmost) element and all
duplicates. It may or may not work as intended on all inputs.
void expungeStack(Stack<int>& stack) {
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int first = stack.peek();
for (int i = stack.size()-1; i >= 0; i--) {
int cur = stack.pop();
if (cur != first) {
stack.push(cur);
}
}
}
}
You create the test cases below to test expungeStack on inputs where the stack’s topmost element
is not duplicated elsewhere in the stack. expungeStack works correctly on both test cases. (Note:
when listing stack elements, the order is bottommost to topmost.
Input stack Expected result Actual result
-------------------------------------------------
{} {} {}
{7, 1, 4} {7, 1} {7, 1}
You now move on to test cases when the stack's topmost element is duplicated.
f) Give an example test case in which the topmost element is duplicated for
which expungeStack works correctly (or write None if there is no such input).
Your test case here:
g) Give an example test case in which the topmost element is duplicated for
which expungeStack does not work correctly (or write None if there is no such input).
Your test case here:
Q4) Recursion Mystery
a) For each of the calls to recursionMystery1 below, indicate the return value:
int recursionMystery1(int a, int b) {
if (a < b) {
return a;
}
return recursionMystery1(a-b, b);
}
Write your answer below:
Call Return value
----------------------------------------------------
recursionMystery1(10,4) Your answer here:
recursionMystery1(3,7) Your answer here:
recursionMystery1(15,5) Your answer here:
b) What mathematical function does recursionMystery1 calculate?
Your answer here:
c) For each of the calls to recursionMystery2 below, indicate what is printed out from the function:
void recursionMystery2(int a, char c) {
if (a != 0) {
cout << c;
if (a % 2 == 0) {
cout << "O";
recursionMystery2(a - 1, c - 1);
} else {
recursionMystery2(a - 1, c + 1);
cout << "R";
}
} else {
cout << endl;
}
}
Note: char ASCII values are in increasing order, e.g., 'a’ + 1 == ‘b’
Write your answer below:
Call Printed value
----------------------------------------------------
recursionMystery2(5, 'f') Your answer here:
recursionMystery2(4, 'i') Your answer here:
Q5) Recursive Functions
Given a string s, compute recursively (no loops) the number of "11" substrings in the string. The "11" substrings should not overlap.
count11("11abc11")returns2.count11("abc11x11x11")returns3.count11("111")returns1.
Your code here:
int count11(string s)
Given a string s, compute recursively (no loops) a new string where all the lowercase 'x' chars have been changed to 'y' chars.
changeXY("codex")returns "codey".changeXY("xxhixx")returns "yyhiyy".changeXY("xhixhix")returns "yhiyhiy".
Your code here:
string changeXY(string s)