|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
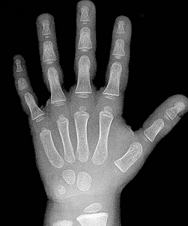
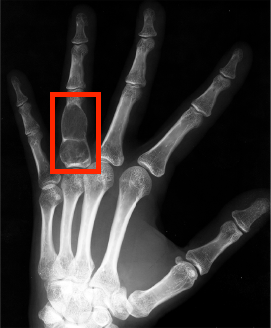
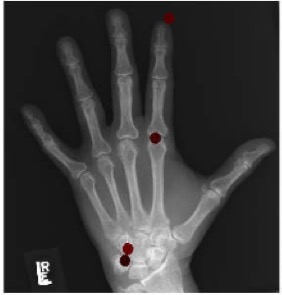
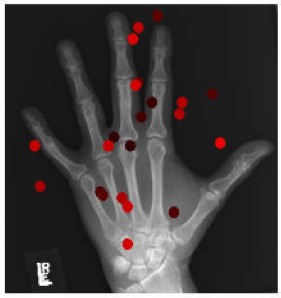
Hand bone age AI
Predict
hand bone age.
Charles
Fang, Saif Baig, David Larson, Michael Fadell, Bao Do
In a small test of 129 random Stanford
clinical cases, AI predicted age within 12 months of the Greulich and Pyle
atlas in 99.2% of cases (128/129), similar to 16bit.ai (96.9%, 125/129). For
educational use. Try it
|
|
|
Stanford Musculoskeletal MRI atlas MSK
anatomy atlas, educational talks, and cases ~1.7M pageviews since 2011
|
|
|
Claripacs.com Web
“zero footprint” PACS for education & research Univ of Calgary Stroke, Stanford MSK & Neuroradiology |
|
|
Leg length AI
Automatic
measurement of leg lengths and angles. Limited generalizability, trained
only @Stanford.
N.
Larson, C. Nguyen, BH. Do, A. Kaul, A. Larson, S. Wang, E. Wang, E.
Bultman, K. Stevens, J. Pai, A. Ha, R. Boutin, M. Fredericson, L. Do, C. Fang Publication.
|
|
|
|
|
|
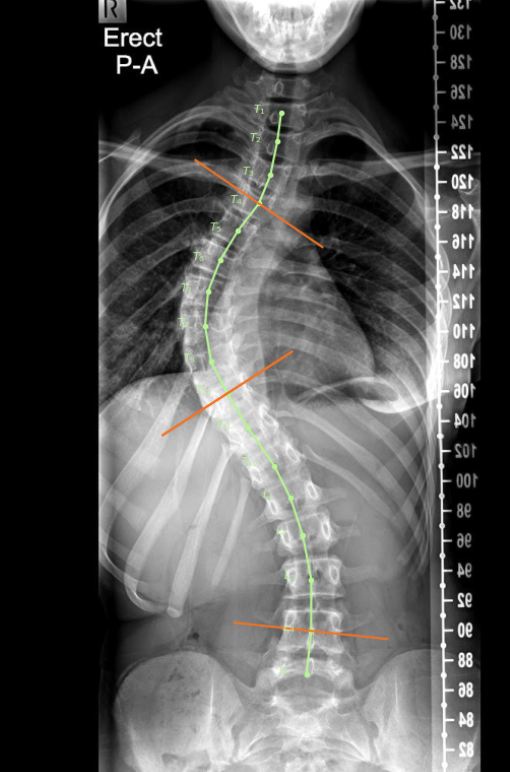
Scoliosis AI Automatic
measurement of spine curves. Limited generalizability, trained only @Stanford. Audrey Y. Ha, Bao H. Do, Adam L. Bartret, Charles X. Fang,
Albert Hsiao, Amelie M. Lutz, Imon Banerjee, Geoffrey M. Riley, Daniel L.
Rubin, Kathryn J. Stevens, Erin Wang, S.W., CF. Beaulieu, Brian Hurt (publication) |
|
|
Automatically write essays
One
of my first computer programs ! |
PROJECTS:
|
|
|
|
|
Nediser AI for Radiology workflow efficiency, eg pre-draft reports,
auto comparison Charles Fang, Bao Do |
|
|
V21 OPPE Administrator Professional
practice evaluation for VHA Audrey
Ha, VHA WOC researcher, Charles Fang, Bao Do |
|
|
|
|
|
Keypoint Annotator Tool
for fast annotation of keypoints for training neural networks to learn angles
and distances btwn points in an image (see below, “Automatic Diagnosis of
Knee Patella Malalignment…” AMIA 2020 Annual Symposium). Aryan
Kaul, Bao Do. |
|
|
Report Miner VA
search engine indexing VistA radiology reports at VA Palo Alto for education
and clinical work. Charles
Fang, Bao Do. |
|
|
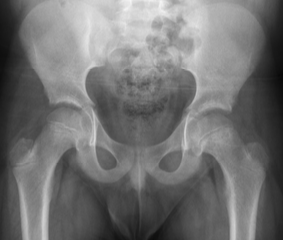
Expert level detection of slipped capital femoral epiphysis
using artificial intelligence Andrew
Campion, Audrey Ha, Bao Do, Charles Fang, Kevin Shea, Michael Fadell. AI
for detection of SCFE in 3 grades, using only the AP view (no frog leg). Internal
test, AI 99% accurate (103/104 cases). Research only, not recommended
for clinical use. International Pediatric Radiology
Congress 2021, Rome, Oct 11-15, 2021 (ipr2021.org) |
|
|
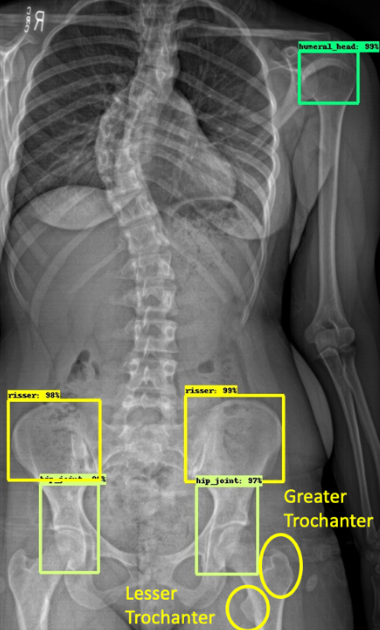
Automatic Extraction of Skeletal Maturity from Whole Body
Pediatric Scoliosis X-rays. Skeletal
maturity assessment plays an important role in the management of pediatric
orthopedic conditions such as scoliosis, slipped capital femoral epiphysis
(SCFE), and pectus. The most common methods to estimate bone age are the
use of hand, shoulder, and/or pelvis x-ray. Can whole body x-rays be helpful
for extracting skeletal maturity estimates (ie, Oxford stage) ? Audrey
Ha, John Vorhies, Andrew Campion, Charles Fang, Michael Fadell II, Steve
Dou, Safwan Halabi, David Larson, Emily Wang, YongJin Lee, Joanna Langner,
Japsimran Kaur, Bao Do. Short paper publication. IEEE BIBM Conference 2020. |
|
|
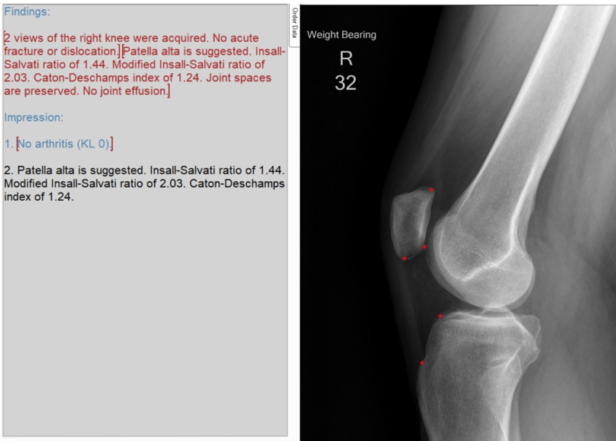
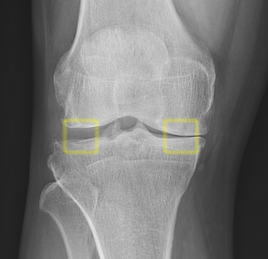
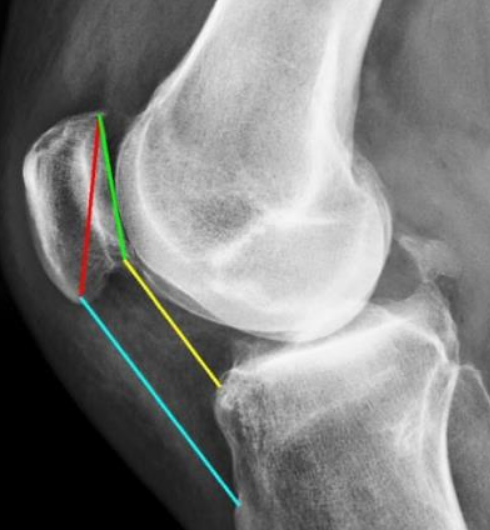
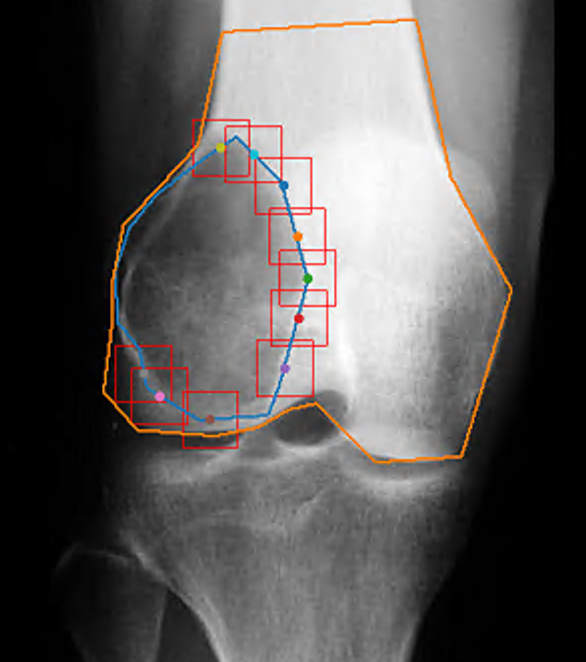
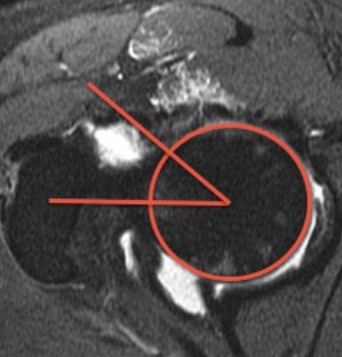
Automatic Diagnosis of Knee Patella Malalignment on X-ray
Using Artificial Intelligence. Measurement of the
Install-Salvati, modified Install-Salvati, and Caton-Deschamps Index on
knee xray exams. In use @ VA Palo Alto. Aryan
Kaul, Jason Pai, Charles Fang, Ed Boas, Kathryn Stevens, Jason Saleh,
Vananh Nguyen, Constance Chu, Jamie Schroder, Michelle Nguyen, Joshua
Reicher, Woon Teck Yap, Amelie Lutz, Bao Do. AMIA 2020 Annual Symposium. |
|
|
Automatic Detection of Aortic Aneurysm on CT Exams Using
Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Audrey
Ha, Charles Fang, Saif Baig, Bao Do. AMIA
2020 Annual Symposium, November, 2020. |
|
|
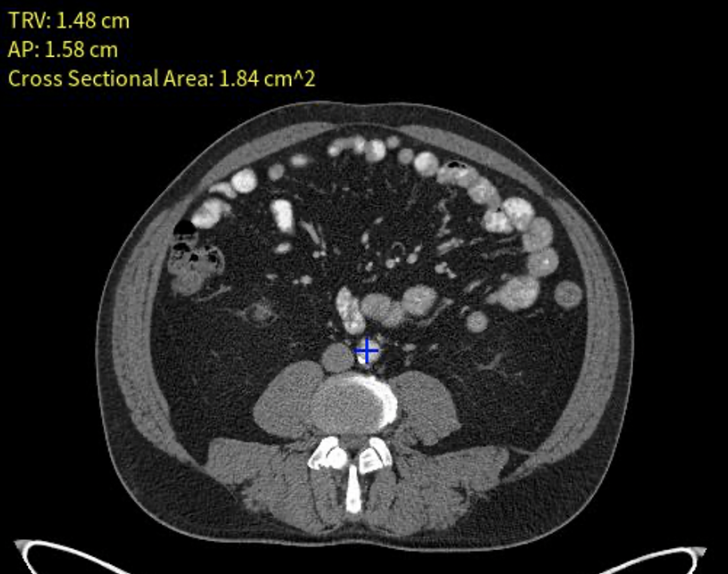
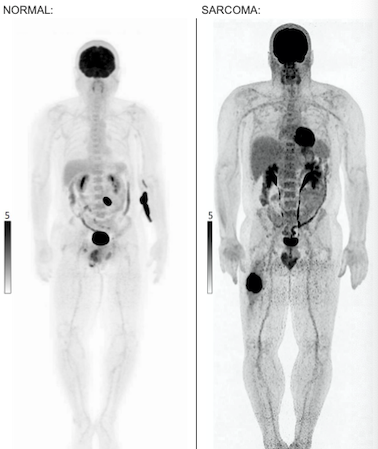
Automatic detetion of thigh sarcoma on whole body PET/CT Brief
experiment for classification on PET images. Limited test 14 (9 tumors + 5
normals), AI 92.8% accurate, F1 score 0.94. Lays foundation for AI based detection,
interpretatation, and reporting of PET and CT/MRI exams, research only. Not
in clinical use. |
|
|
Precision diagnosis of bone tumors on radiography using deep
learning and bayesian network demo AI
for generating ddx of bone tumors on xray using computer vision and a
bayesian probabilistic network |
|
|
Radiology
mangement software for the Veteran’s Health Administration. Joshua Reicher, Payam Massaband, B. Do link License
link |
|
|
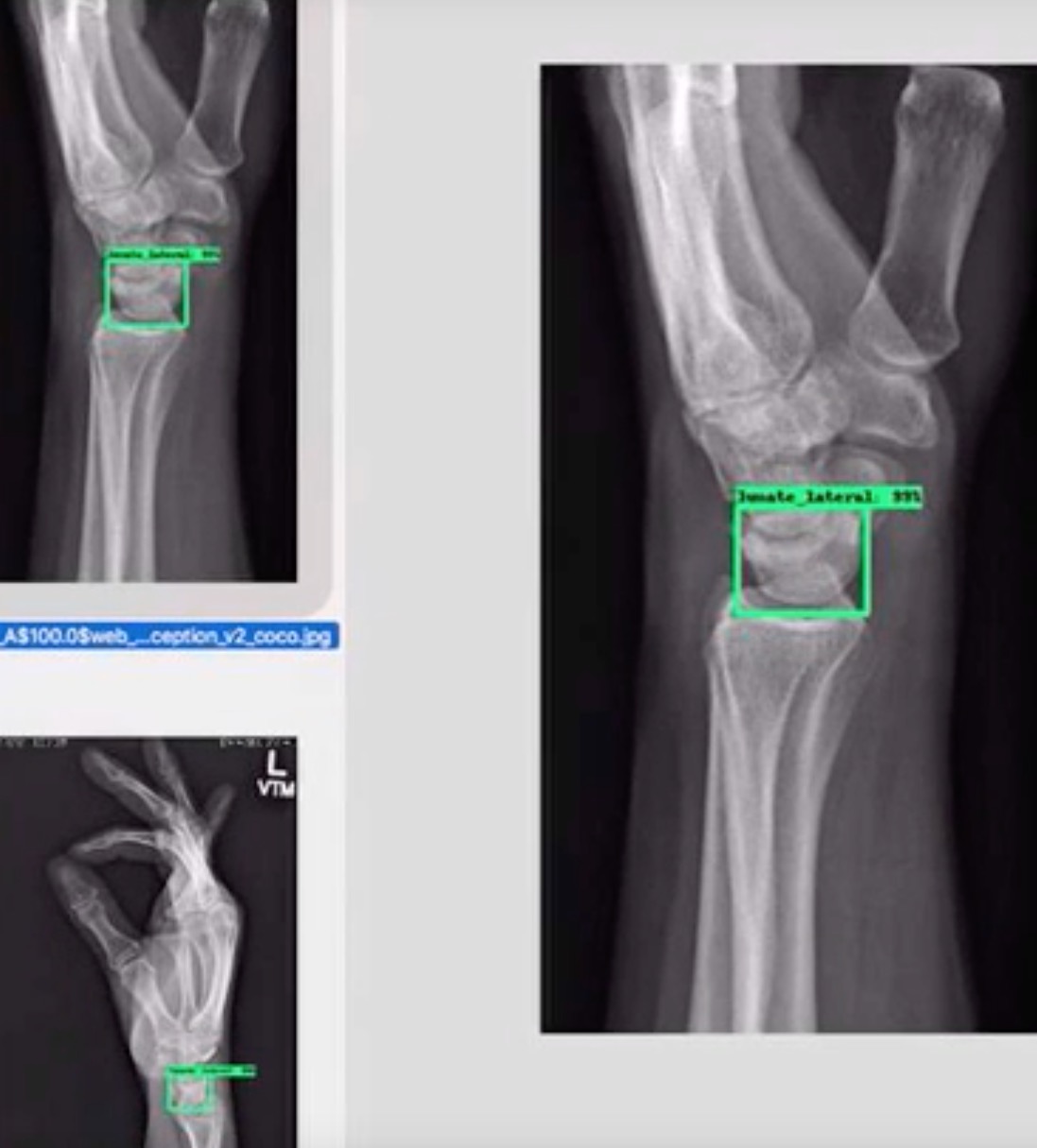
Deep learning of wrist bone xray exams for trauma. Machine Learning-Aided Diagnosis
Enhances Human Detection of Perilunate Dislocations. 75th ASSH Annual Meeting,
San Francisco. October 1-3, 2020. |
|
|
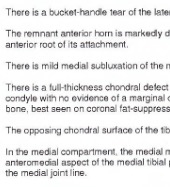
“Expert” level perception of ACL trauma on knee xray exams
using sparse data. A.I. automatic diagnosis of a subtle x-ray finding (Segond
fracture, less than 0.04% of entire area of an image) using contextual interpretation,
like a radiologist. Machine was 100% accurate (F-score 1.0) in our limited 20
test samples. Science poster presentation RSNA 2018. |
|
|
Detection
and characterization of peri-articular calcification using deep learning Potentially for automatic quantification and
calcinosis staging. |
|
|
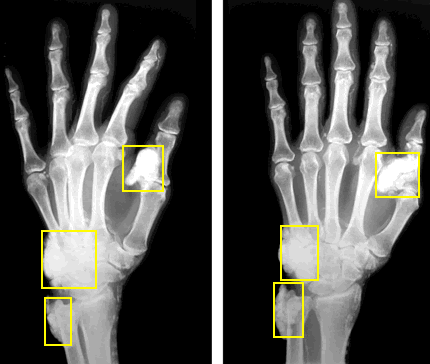
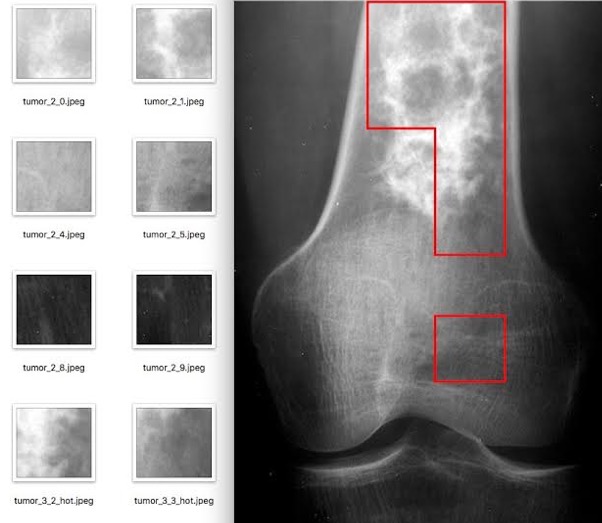
Automatic
chondroid bone tumor detection using deep learning Can
machines identify tumors such as chondroid mass ? This is a simple patch
based CNN that was slow and not particularly sensitive or specific. |
|
|
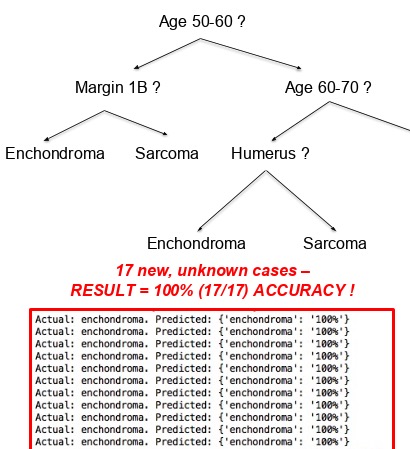
Machine
learning decision trees in radiology Experiment
using A.I. to automatically build expert decision trees from radiology
observations to partition tumor classes. 100% accuracy in limited testing
but broad application (classify 10+ tumor dxs, 15+ observations per dx) was
plagued w/ over-fitting due to small sample size at this time. |
|
|
IVC
filter machine learning Teach
computer to recognize IVC filters on x-ray images [ article ]. |
|
|
|
|
|
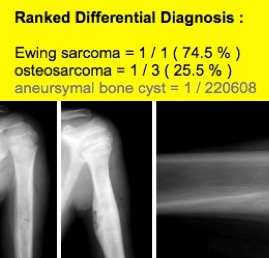
Chondroid
machine Adapted
Stanford Bone Bayes engine to discriminate benign (enchondroma) VS
malignant (chondrosarcoma) chondroid bone tumors. Preliminary performance
exceeded >85% of radiologists. Do, BH, Beaulieu CF, Human VS Machine: Distinguishing Enchondroma from Chondrosarcoma
with a Bayesian Network, Society of Skeletal Radiology meeting, 3/2018.
Rec’d SSR “Man Vs Machine” Award, 2018. |
|
|
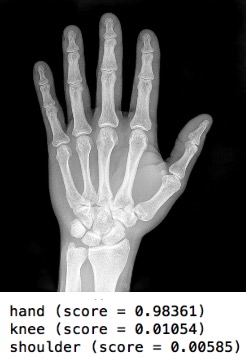
DeepBone
Deep
convolutional neural net to identify bone joints of the human body.
Foundation for PACS comparison protocols, automated decision systems such bone
tumor diagnosis, information retrieval, QA, etc. Dr. Vossler rec’d a
Student Travel Award for Young Investigators at the RSNA 2017 Scientific Meeting. |
|
|
Stanford
Bone Bayes A
“learning” Bayesian network that models clinical and radiographic inputs to
compute diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and probabilities. link publication |
|
|
Co-founded
secure cloud PACS that can be customized for clinical care, education, research, media
reports. More than 100,000 users have now viewed > 10 million images on clariPACS.
Highlights: Univ of Calgary Stroke
findings and Stanford
Neuroradiology |
|
|
Community of radiologists promoting the exchange
of high level musculoskeletal imaging expertise. Searchable gallery of
common and rare musculoskeletal disorders for decision support, teaching.
Founded by Philip Tirman MD (2003). Served > 1 million images since
2010. |
|
|
Stanford Atlas of Common MSK Measurements RadLex-enabled
atlas of common MSK measurements. Designed to leverage RadLex ID interoperability
for automation systems. RSNA Scientific Meeting, 2010. |
|
|
ACGME
Analytics To eliminate the labor intensive task
of counting Radiology residency workloads at VA centers by mining VistA to
generate an ACGME compliant summary of workload by CPTs. The Accreditation
Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) requires bi-annual case log
statistical reports by Residency programs for all medical specialties. The
Residency Review Committee (RRC) for Radiology recognizes 90 CPT codes in
11 categories: chest radiographs, CT body, CT angiography, image guided biopsy
and drain, mammography, MRI body, MRI brain, MRI knee, PET/CT, ultrasound
pelvis, and MRI spine. |
|
|
Hedge
Detector Automatic
extraction of uncertainty and recommendation concepts from unstructured radiology
reports. Applications include for QA, follow-up, peer review, disease
surveillance. Rec’d RSNA Research Trainee Prize for Scientific Paper, RSNA
Scientific Meeting, 2009. |
|
|
VA Radiology Analytics Mine
and summarize operations metrics for VA Hospitals using VistA radiology
data. Common metrics to help identify bottlenecks in radiology clinical operations
at Veteran hospitals. |
|
|
Free
MRI atlas of musculoskeletal radiology. Has
served > 600,000 pages & > 20 million+ images to users from 100+
countries since 2011. RSNA Scientific Meeting, 2010. |
|
|
Radiology report search engine, originally indexed
nearly 1,000,000 cases in Stanford radiology. Shared for free to numerous academic
institutions, hospitals, and individuals around the world, including deployment
at Hospital de Pediatria J. P. Garrahan, a children’s hospital in Buenos
Aires, Argentina (Darío Filippo MD), where it enables search of over 250,000
radiology, pathology, and surgery notes. Interesting
behaviors in medical imaging search. RSNA Scientific Meeting,
2009. |
|
|
iKeyNote Audience
response system w/ MCQ style interactive polling for Stanford radiology
lectures. |
|
|
NLP to
structure MSK MRI knee reporting Auto
structured knee MRI reports from free dictation in real time. RSNA
Scientific Meeting, 2010. |
|
|
NLP to
detect missing concepts in MSK tumor reporting May
augment self learning systems via extraction of ground truth correlation of
RIS/PATHOLOGY. RSNA Scientific Meeting, 2012. |
|
|
NLP to
automate quality assurance using RIS reports - Fractures Fully
automatic extraction of accuracy statistics from unstructured radiology
report data using NLP to compare knee x-ray reads against the follow-up
MRI/CT reports as ground truth. QA, education, teaching, peer review. RSNA
Scientific Meeting, 2011. |
|
|
NLP to
automate quality assurance using RIS reports - Osteoporosis Automatically
extract accuracy metrics for osteoporosis from radiology reports in the
RIS, using NLP to compare against the follow-up DEXA reports, respectively,
as ground truth. RSNA Scientific Meeting, 2011. |
|
|
NLP to
derive central line usage from unstructured ICU x-ray reports Using
NLP to build an ICU patient consensus and central line indwelling estimate
from unstructured chest x-ray reports. |
|
|
Feedback NLP of fractures in
unstructured reports of ED studies Real-time
retrieval of fracture classifications and clinical pearls extracted from free
dictation for decision support. Rec’d RSNA Research Trainee Prize for
Scientific Paper, RSNA Scientific Meeting, 2007. |
|
|
Characterizing radiology
search patterns using web analytics System
to analyze how radiologists review studies using heat maps of mouse
movement and magnification patterns, deployed completely via the web. Note
how experienced, attending radiologists (LEFT) require fewer mouse
movements and magnification compared to trainee radiology residents (RIGHT).
Deployed in online simulator of call cases for residents. RSNA Scientific
Meeting, 2008. |
|
SELECTED
PUBLICATIONS: Do,
B. H., Wu, A. S., Maley, J., & Biswal, S. (2012). Automatic
Retrieval of Bone Fracture Knowledge Using Natural Language Processing.
Journal of Digital Imaging, 26(4), 709–713. http://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-012-9531-1 Do,
BH, Langlotz, C, Beaulieu, CF. Bone Tumor Diagnosis Using a Naïve
Bayesian Model of Demographic and Radiographic Features. Journal of
Digitial Imaging. 2017 Jul 27. doi: 10.1007/s10278-017-0001-7. Ni JC, Shpanskaya K, Han M, Lee EH, Do BH,
Kuo WT, Yeom KW, Wang DS. Deep-Learning for Automated Classification
of Inferior Vena Cava Filter Types on Radiographs. J Vasc Interv
Radiol. 2019 Sep 18. pii: S1051-0443(19)30536-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2019.05.026. Enamandram, S. Sandhu, E. Do, BH, Reicher,
JJ., Beaulieu, CF. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Applications in Musculoskeletal Imaging. Advances in Clinical
Radiology. 28 May 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yacr.2020.05.005 Audrey Ha, John Vorhies, Andrew Campion,
Charles Fang, Michael Fadell II, Steve Dou, Safwan Halabi, David Larson, Emily
Wang, YongJin Lee, Joanna Langner, Japsimran Kaur, Bao Do. Automatic Extraction of Skeletal Maturity from Whole Body
Pediatric Scoliosis X-rays Using Regional Proposal and Compound Scaling Convolutional
Neural Networks. Short paperpublication. IEEE International Conference on
Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), 12/2020. Ha,
AY., Do, BH, Bartret, AL, Fang, CX, Hsiao, A., Lutz, AM, Banerjee, I.,
Riley, GM., Rubin, DL., Stevens, KJ, Wang, E., Wang, W., Beaulieu, CF.,
Hurt, B. Automating scoliosis measurements in radiographic studies
with machine learning: Comparing artificial intelligence and clinical
reports. Journal of Digital Imaging, Feb 2022. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10278-022-00595-x Larson,
N., Nguyen, C., Do, B., Kaul, A., Larson, A., Wang, S., Wang, E., Bultman,
E., Stevens, K., Pai, J., Ha, A., Boutin, R., Fredericson, M., Do, L.,
Fang, C. Artificial Intelligence System for Automatic Quantitative Analysis
and Radiology Reporting of Leg Length Radiographs. J Digit Imaging
July 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-022-00671-2. |
|
|
|
|