Poxviridae contains two subfamilies: the Chordopoxvirinae, which has eight genera and infects a wide range of mammals and birds, and the
Entomopoxvirinae with three genera that affect only insects. The following poxviruses affect humans:
|
· Variola · Vaccinia · Cowpox · Monkeypox · Bovine papular stomatitis · Orf · Pseudocowpox · Molluscum contagiosum · Tanapox · Yabapox |
|
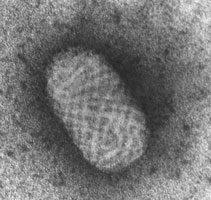
Smallpox, caused by variola virus, has led to at least three "firsts:" the first vaccine, the first disease to be eradicated by immunization, and the first virus infection against which chemotherapy was clinically effective. In the past few years, many other "firsts" have taken place in this viral family: monkeypox emerged in the Western Hemisphere and the first case of inadvertent contact vaccinia transmission from a breasfeeding mother to infant was reported. Smallpox, although eradicated, infiltrated our homes, as politicians discussed the potential for a bioterror attack and whether to vaccinate or not to vaccinate the people of the United States.
Poxviridae is a "complex" family of viruses: morphologically, politically, economically, and socially. So go ahead, explore and learn a lot more about Poxviridae!