Practical combustors also involve multiphase systems where the fuel is injected as a liquid jet that breaks up to form secondary droplets. These droplets then evaporate to form the gas-phase fuel that passes through the combustion zone. In addition, fuel rich high temperature regions can cause soot formation that leads to solid particle evolution inside a combustor. Such multiphase multi-physics phenomena can be captured by a modular modeling approach. Different physical regimes of the combustor, namely primary breakup, secondary atomization, combustion, soot formation can be studied using independent target cases.
Droplet Evaporation in a Temporal Shear Layer
Click image to see full size.
Droplet evaporation in a temporal shear layer (Re=200). Droplet position superimposed on mixture fraction contours. 5 million hexane drops are simulated in this direct numerical simulation.
Click here to see animation.
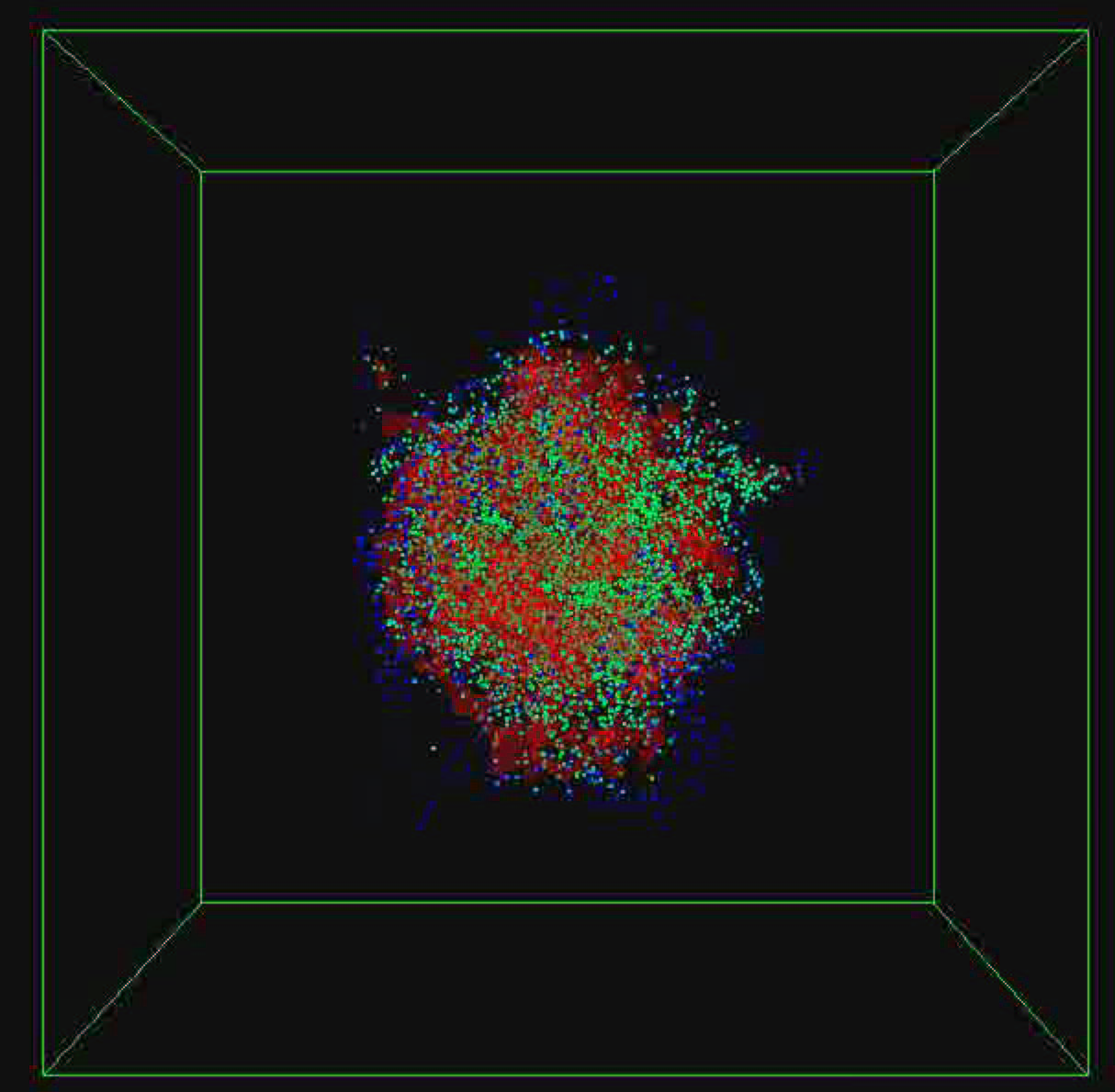
Ignition of a Cluster of Heptane Droplets
Ignition of a cluster of heptane droplets. Droplet position superimposed on an isosurface at T=2200K.
Click here to see animation.
Preferential Concentration of Particles in a Turbulent Mixing Layer
Preferential concentration of particles in a turbulent mixing layer (Re=200). The Stokes number for these particles is 3. Vorticity contours are shown. Long particle beads are seen forming in regions of high strain, low vorticity.
Click here to see animation.