|
To
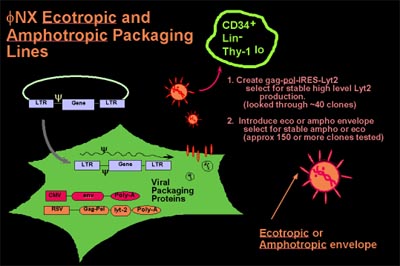
overcome these obstacles ourlaboratory created new packaging
lines, termed Phoenix, and made several improvements to them
over the first generation approach (15). Two cell lines were
created, Phoenix-ECO and Phoenix-AMPHO. Additionally, a line
termed Phoenix-gp has been produced that expresses only gag-pol.
This
line is available for further pseudotyping of retroviral virions
with other envelope proteins such as gibbon ape leukemia virus
envelope or Vesicular Stomatitus VSV-G protein, xenotropic,
or retargeting envelopes can also be added.
Both
Phoenix-ECO and Phoenix-AMPHO were tested for helper virus production
and es tablished as being helper-virus fre and are fully compatible
with transient, episomal stable, and library generation for
retroviral gene transfer experiments (15):
All lines are capable of carrying episomes for long-term stable
production of retrovirus (see below). All lines are readily
testable by flow cytometry for stability of gag-pol (CD8) and
envelope expression; (after several months of testing the lines
appear stable, and do not demonstrate loss of titre as did the
first-generation lines BOSC23 and Bing. The new lines are more
stable we think partly due to the choice of promoters driving
expression of gag-pol and envelope).Both lines can also be used
to transiently produce virus in a few days.Thus we have the
means to deliver large libraries of retroviruses into nearly
any mammalian cell type, mouse or human.
Finally, we have tested the titres produced by these lines.
Using standard polybrene-enhanced retroviral infection we observe
titres approaching or above 10^7 per ml for both Phoenix-eco
and Phoenix-ampho when carrying episo mal constructs (see below).
When transiently produced virus is made, titres are usually
1/2 to 1/3 that value.
|