CS 101
Core Application Components
Plan for Today
- Recall: requests go to a server, which returns a response
- Recall: servers store information in databases
- Today: how do applications work?
- Distributed Systems
- Databases
- APIs
- Code in the Real-World
Another note about ads
Distributed Systems: Theory
- Problem: more memory is expensive; more CPU is expensive
- Idea: link a bunch of cheap computers together into a "giant" computer
- Have each computer solve a tiny part of the problem
- Have each computer store part of the problem
- Challenges of Distributed Systems:
- Sometimes, computers fail
- Need to store information across multiple computers
- Need to wait for all computers to finish calculations
MapReduce
- Idea: make a faster CPU that can execute many instructions at the same time
- Each computer solves part of the problem
- Famous example: WordCount
Distributed System: Databases
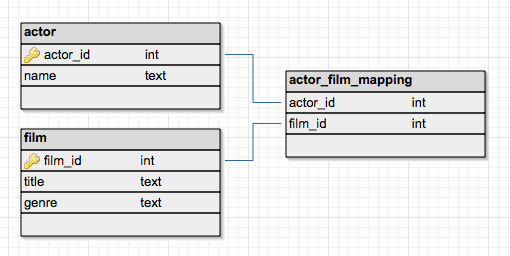
- (Usually) stored across many computers (distributed system)
- Added benefit: can spatially disperse the knowledge
- Recall: like a giant Excel sheet, but with millions/billions/trillions of rows
- Databases are made of tables. Each table represents one object
- Relationships between different tables
- Example: Table of superheroes, and another table of Marvel Movies. Each superhero is in a Marvel movie.
AWS
- Amazon Web Services
- How Amazon makes money ($17.46 billion in revenue in 2017)
- Amazon manages servers (cheaper for small websites) - easily scales
- Amazon S3 - storage by Amazon (e.g. Piazza)
- Easy way to host a website - make it available on the internet
APIs
Formatting Data
- Data has to be organized well to easily extract information
- APIs need to return data in a well-organized way
- Commonly use JSON (JavaScript Object Notation); alternative is XML
- Structured way to determine what information exists and its form
"class": {
"name": "CS101",
"students": ["Ashley", "Shreya"],
"location": {"building": "Gates", "number": "B12", "capacity": 50}
}
Code in the Real-World
- Writing code "in production" presents lots of challenges
- Talk with a neighbor about the challenges a large company like Facebook would have to overcome
Code in the Real-World
- How do we know that code works? Testing
- Unit tests
- Integration tests
- Development servers
- How do we handle multiple people editing code at the same time? Version Control (GitHub)
Green Screen Contest
- Vote for funniest and most artistic
- Slide Show