Lecture Preview: Binary Trees
(Suggested book reading: Programming Abstractions in C++, Chapter 16, section 16.1)
Today we'll learn about a way of organizing data in memory called a binary tree. A binary tree shares some aspects of the linked list that you have just studied. Just like linked list has two parts that work together: ListNode (holds a piece of data and a "next" pointer) and LinkedList (holds a pointer to only the first node of the list, from which we can traverse and access the whole list), binary trees have a TreeNode and BinaryTree that work together.
Definitions:
- tree: hierarchical structure of linked nodes.
- binary tree: a tree where each node has at most two children
- Recursive definition: A tree is either:
- empty (NULL), or
- a root node that contains: (1) data, (2) a left subtree, (3) a right subtree
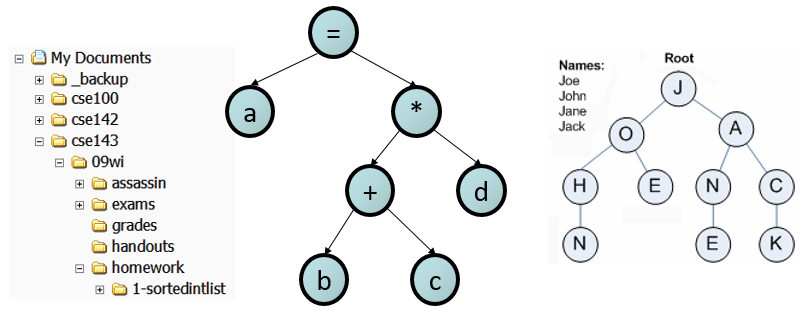
Trees are useful throughout computer science. For example, the folders (directories) on a computer form a tree structure--each folder can contain more folders. Note that folders form a tree structure but not necessarily a binary tree structure, because a folder may have more than two sub-folders contained within it. Other tree structures include a family genealogy, a corporate organizational chart, (in AI) a decision tree, (in compilers) a parse tree ("a = (b+c) * d;"), or cell phone word auto-completion.
Binary tree terminology:
- node: an object containing a data value and left/right children
- root node: topmost node of a tree (the parent of all the others)
- subtree: the smaller tree of nodes on the left or right of the current node
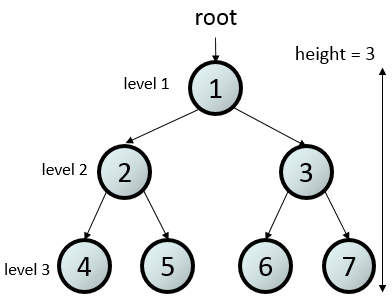
- tree height: number of nodes from the root to the furthest descendant of that node
- tree level or depth [of a node]: number of nodes from the root to that node