Lecture Preview: Stacks and Queues
(Suggested book reading: Programming Abstractions in C++, section 5.2 - 5.3)
In this lecture we will talk about two new data structures:
-
A stack is a collection where you add elements to the "top" of the ordering, and remove from the "top" as well. The only accessible element is the one added latest. A stack is sometimes called a Last In, First Out ("LIFO") structure.
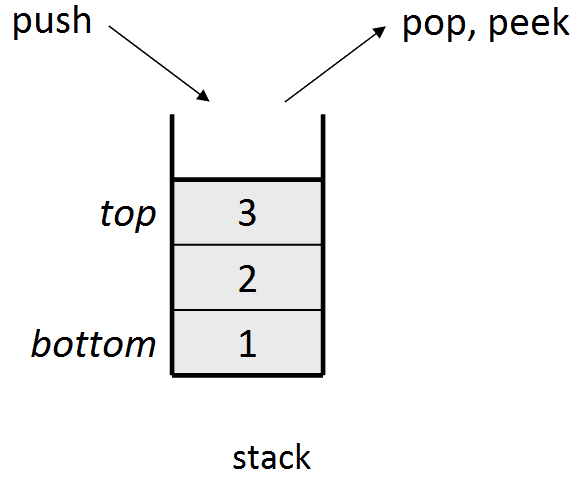
-
A queue is a collection where you add elements to the "back" of the ordering, and remove from the "front" of the ordering. The only accessible element is the one added earliest. A queue is sometimes called a First In, First Out ("FIFO") structure.
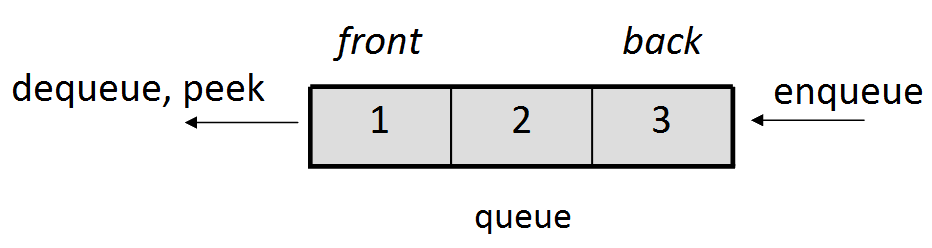
When you declare a stack or queue, you write the type of data it will contain in < > brackets.
Here is a short code example that uses a stack:
Stack<int> s; // {} bottom -> top s.push(42); // {42} s.push(-3); // {42, -3} s.push(17); // {42, -3, 17} cout << s.pop() << endl; // 17 (s is {42, -3}) cout << s.peek() << endl; // -3 (s is {42, -3}) cout << s.pop() << endl; // -3 (s is {42})
Here is a short code example that uses a queue:
Queue<int> q; // {} front -> back q.enqueue(42); // {42} q.enqueue(-3); // {42, -3} q.enqueue(17); // {42, -3, 17} cout << q.dequeue() << endl; // 42 (q is {-3, 17}) cout << q.peek() << endl; // -3 (q is {-3, 17}) cout << q.dequeue() << endl; // -3 (q is {17})
